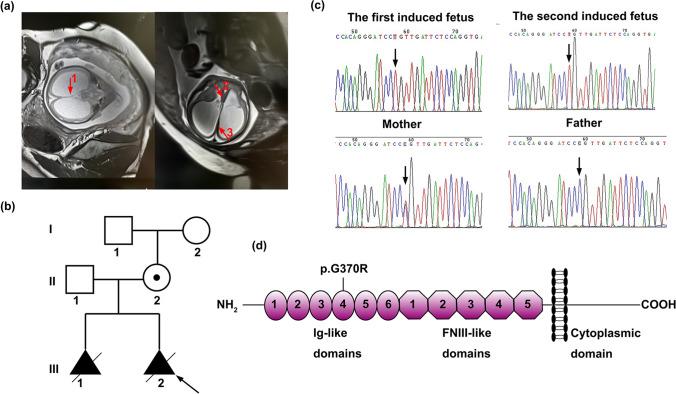
Fig. 1.
Clinical characteristics of family and schematic model of L1CAM molecule. a Magnetic resonance imaging of the second induced fetus (abnormal fetus). The absence of the cavum septi pellucidi is indicated by arrow 1 in the coronal plane. The corpus callosum agenesis is indicated by arrows 2 and 3 in the axial plane. b Pedigrees of the analyzed family in this study. Males are represented by squares, females are represented by circles, and triangle refers to abortion in early pregnancy. The proband is indicated by an arrow. c Sanger sequences of the L1CAM gene mutation (c.1108G > A). Hemizygous mutation detected in two induced fetuses (abnormal fetuses). The heterozygous mutation detected in these fetuses’ mother but not in these fetuses’ father. Mutation was indicated by arrow. d Schematic model of L1CAM molecule bearing domain structure: six immunoglobulin-like motifs (Ig-like), five fibronectin type III (FNIII)-like domains, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular domain (ICD). The location of the amino acid substitution (p.G370R) is indicated