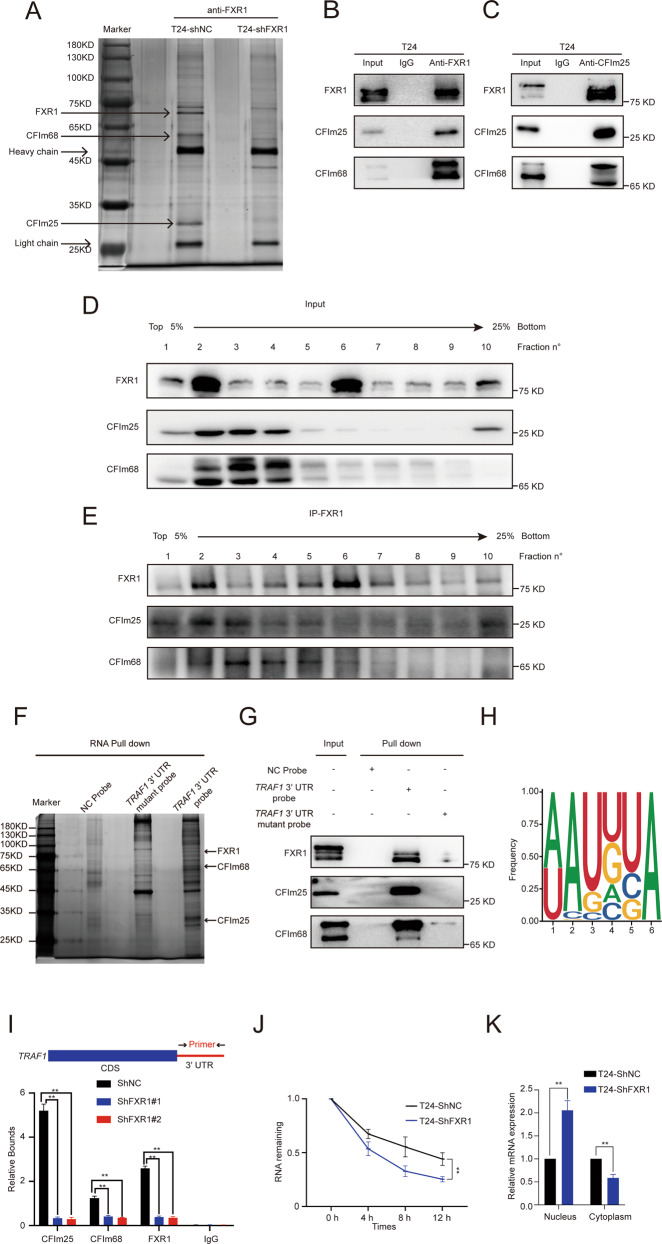
Fig. 5. FXR1 recruits CFIm25 and CFIm68 forming a novel complex of mRNA 3′ end processing machinery at the TRAF1 transcript.
A Silver staining illustrated the Flag-tagged FXR1 complex in T24 cells. B, C Co-IP of FXR1-interacting complex or CFIm25-interacting complex in T24 cells. D Western blot showing the distribution of FXR1, CFIm25, and CFIm68 sedimented through a 5-25% glycerol gradient in T24 cells. E Western blot showing the distribution of the FXR1-interacting complex-sedimented through a 5-25% glycerol gradient in T24 cells. F, G Silver staining (F) and immunoblot (G) illustrated TRAF1 3′ UTR pull-down protein in T24 cells. H UGUA RNA binding motif analysis from FXR1 RIP-seq. I ChIP and RT-qPCR analysis showed the recruitment of FXR1, CFIm25, and CFIm68 to the TRAF1 3′ UTR in control or FXR1 depleted cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3, **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). J qRT-PCR analysis revealed the short half-life of TRAF1 mRNA in control or FXR1 knockdown cells after treatment with actinomycin D. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3, **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). K qRT-PCR analysis showed the cellular distribution of TRAF1 mRNA in control or FXR1 knockdown cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3, **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test).