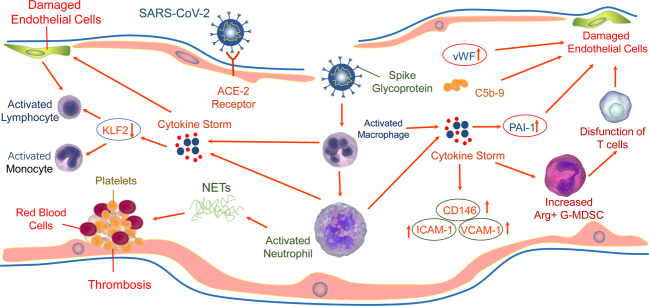
Fig. 2.
Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 induced to endotheliopathy in COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 directly invades endothelial cells or indirectly induces cytokine storm to cause endothelial cell damage. On the one hand, the SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 expressed on the surface of endothelial cells can be directly invaded by the virus. On the other hand, cytokine storm destroys endothelial cells by inducing the release of PAI-1, promoting the degradation of endothelial glycocalyx to release HA fragments and destroying the endothelial barrier; downregulating the expression of KLF2 to induce adhesion and infiltration of monocytes/macrophages, or by immune dysregulation such as increased NETS generation and T-cell dysfunction. Finally, endothelial dysfunction could be further aggravated by complement activation, thrombosis, coagulation disorders and activation of immune cells. Meanwhile, circulating endothelial injury markers including vWF and sCD146 were elevated