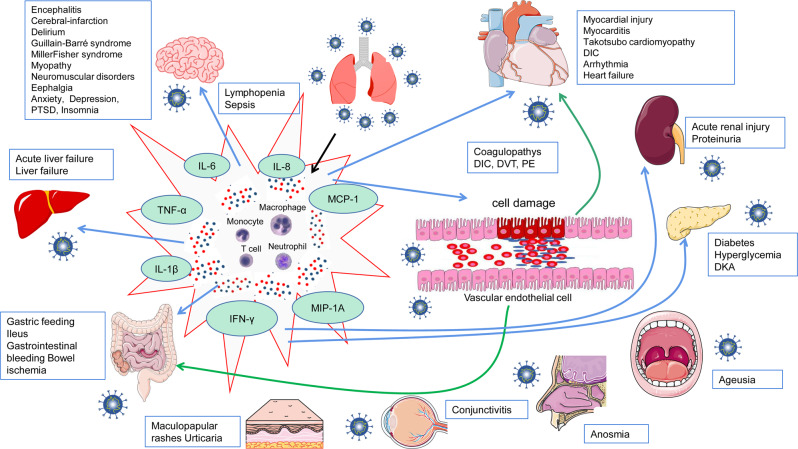
Fig. 3.
The extrapulmonary complications of COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 infection has resulted in not only a pulmonary disease but also potentially systematic disease, which may cause long-term multiple organ-system complications including hyperinflammatory syndrome, vascular thrombosis, coagulopathy, cardiovascular, hepatobiliary, gastrointestinal, renal, neurologic, endocrinologic, ophthalmologic, nasal, oral, and dermatologic systems. Proposed mechanisms of the involvement of different organs or systems for COVID-19 caused by infection with SARS-CoV-2 include: direct viral toxicity through interaction of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with the entry receptor ACE2; dysregulation of the immune response, T-cell lymphodepletion and hyperinflammation; endothelial cell damage and thromboinflammation. COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, DIC disseminated intravascular coagulation, PE pulmonary, DVT deep venous thrombosis, DKA diabetic ketoacidosis, PTSD post-traumatic stress disorder