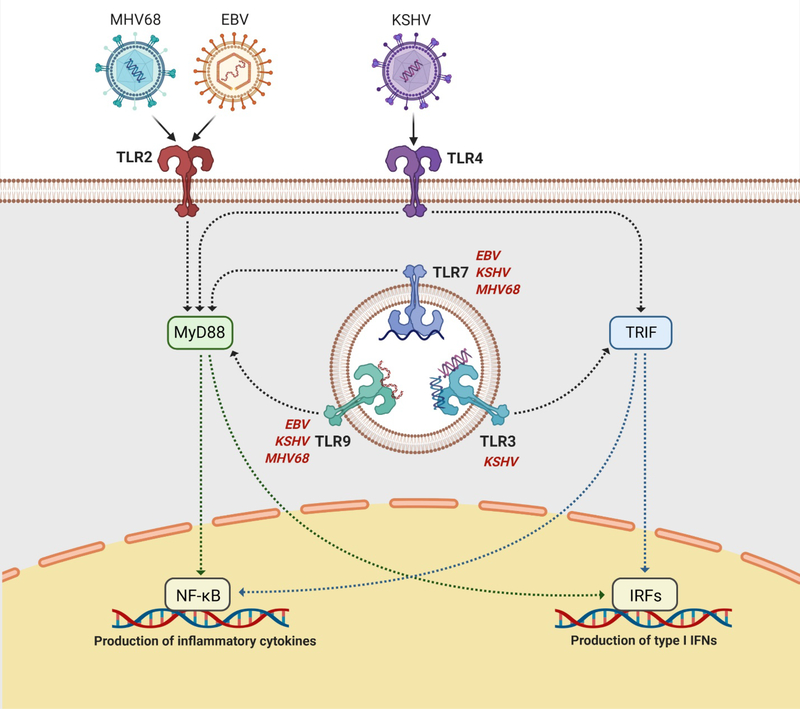
Fig. 2. Gammaherpesvirus infection can be sensed by multiple TLRs including TLRs 2, 3, 4, 7, and 9.
TLRs 2 and 4 are present on the plasma membrane and recognize viral lipids and proteins, while TLRs 3, 7, and 9 are intracellular sensors embedded within endosomal compartments and recognize viral DNA and RNA. Signaling through TLRs is mediated through the adaptor proteins TRIF (TLRs 3 and 4) or MyD88 (TLRs 2, 4, 7, and 9). TRIF recruits downstream proteins which lead to the activation and nuclear translocation of various IRFs, which transcribe type I IFNs. MyD88 recruits downstream proteins which lead to the activation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB, which transcribes proinflammatory and antiviral cytokines. TLRs 7 and 9 have been demonstrated to sense KSHV, EBV, and MHV68 infection, while TLRs 3 and 4 have been shown to be involved in KSHV detection and TLR2 has been shown to be involved in both EBV and MHV68 detection. TLR, Toll-like receptor; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; IRF, interferon regulatory factor. Adapted from “TLR Signaling Pathway” by BioRender.com (2021). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates.