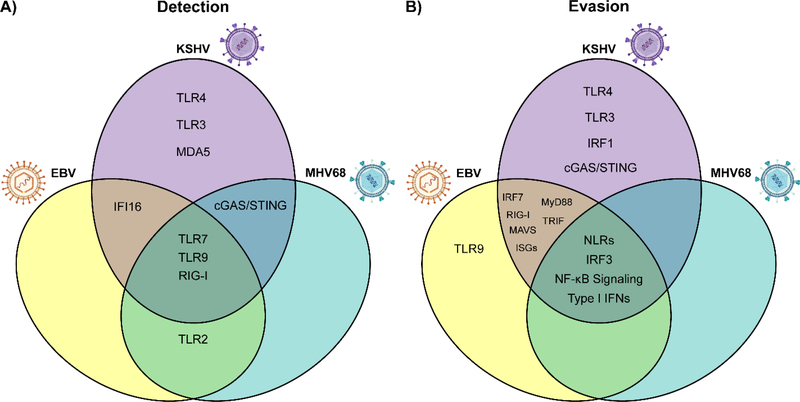
Fig. 4. Shared and differential innate immune sensing of and evasion by gammaherpesviruses.
(A) Sensing of gammaherpesvirus infection occurs through shared and differential innate immune pathways. (B) Similarly, gammaherpesviruses utilize conserved and unique mechanisms to circumvent antiviral innate immune signaling. Importantly, this figure summarizes only the detection and evasion strategies discussed in this review, and the relationships between gammaherpesviruses and innate immune signaling pathways remain incompletely characterized. TLR, Toll-like receptor; IFN, interferon; cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; ISGs, interferon stimulated genes; IFI16, interferon gamma-inducible protein 16; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; IRF, interferon regulatory factor.