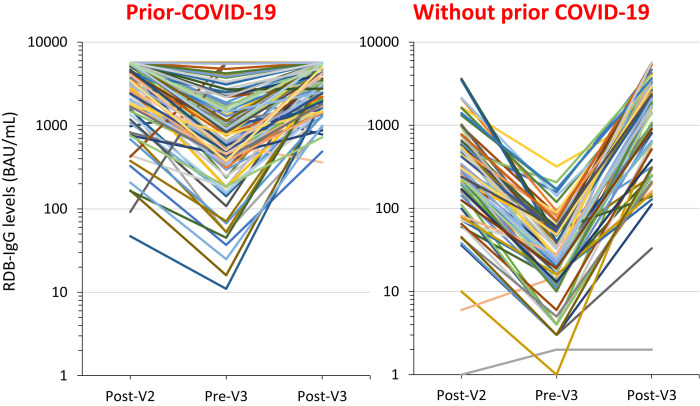
Fig. 1.
Individual change in RBD-IgG levels between 21 and 28 days after the second BNT162b2 vaccine dose (Post-V2), 1-3 days before the third vaccine dose (Pre-V3), and 21-28 after the third vaccine dose (Post-V3) of residents with or without confirmed prior COVID-19. Between March 2019 and September 2021, residents from nursing homes facing a COVID-19 outbreak had repeated RT-qPCR testing until no new cases were diagnosed. Residents from 18 nursing homes having faced a COVID-19 outbreak in 2020 were proposed to undergo blood testing (i) to follow their post-BNT162b2 vaccine response using SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domain (RBD-IgG) levels (IgG II Quant assay, Abbott Diagnostics; upper limit: 5680 BAU) and (ii) to determine if they had prior COVID-19, using IgG antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (N Protein-IgG) (Abbott Alinity; positive level when above 0.8 S/CO). Blood testing when an informed consent was obtained was performed 21-28 days after the second vaccine dose, 1-3 days before the third dose, and 21-28 days after the third dose in order to make comparisons possible in every resident. To make the illustration more readable, the change in values of RBD-IgG levels 21-28 days after the second vaccine dose, before the third dose administered 6 months after the second dose, and 21-28 days after the third vaccine dose are presented for 100 residents with and 100 residents without prior COVID-19. These residents were drawn at random from the 122 with and the 296 without confirmed prior COVID-19.