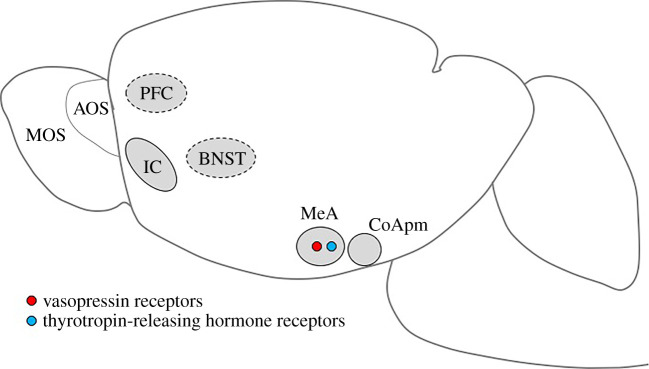
Figure 1.
Brain areas involved in pathogen recognition and avoidance by rodents. The red circle represents vasopressin receptors and the blue circle represents TRH receptors. Although several neurochemicals have been identified to be involved in pathogen recognition and avoidance (oxytocin, opioids, serotonin, dopamine, endocannabinoids, glucocorticoids, various immune components, oestrogens and progesterone), their brain sites of action and the receptors mediating those effects remain unknown. In dashed lines are likely candidate regions. MOS = main olfactory bulb; AOS = accessory olfactory system; PFC = pre-frontal cortex; IC = insular cortex; BNST = bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; MeA = medial amygdala; CoApm = posteromedial nucleus of the cortical-amygdala.