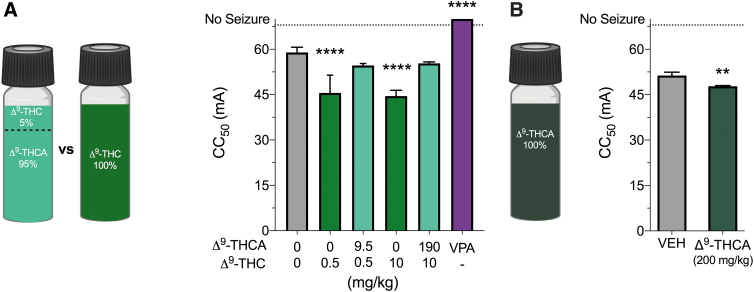
FIG. 4.
The effects of Δ9-THCA in the MEST test. (A) A Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture and pure Δ9-THC were used in the MEST acute seizure model. Cannabinoid content of the Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture was 95% Δ9-THCA and 5% Δ9-THC. The CC50 exhibits a seizure with maximal hindlimb extension after acute i.p. treatment with vehicle (VEH, gray bar), pure Δ9-THC (green bar), a Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture (light green bar), or sodium valproate (VPA, purple bar). Dose of pure Δ9-THC matches that in the Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture. Δ9-THC (0.5 and 10 mg/kg) significantly reduced the CC50 threshold for MES seizures. Sodium valproate (300 mg/kg) treatment protected mice from MES-induced tonic extension. Error bars represent SEM, with n=12 per treatment (****p<0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc compared with vehicle-treated mice). (B) The MEST test was repeated to compare CC50 values after treatment with vehicle (VEH, grey bar) or 200 mg/kg pure Δ9-THCA (dark green bar) that contained <0.5% Δ9-THC impurity. Δ9-THCA treatment significantly reduced the CC50 compared with vehicle treatment. Error bars represent SEM, with n=12 per treatment (**p<0.01; Student's t-test). MEST, maximal electroshock threshold.