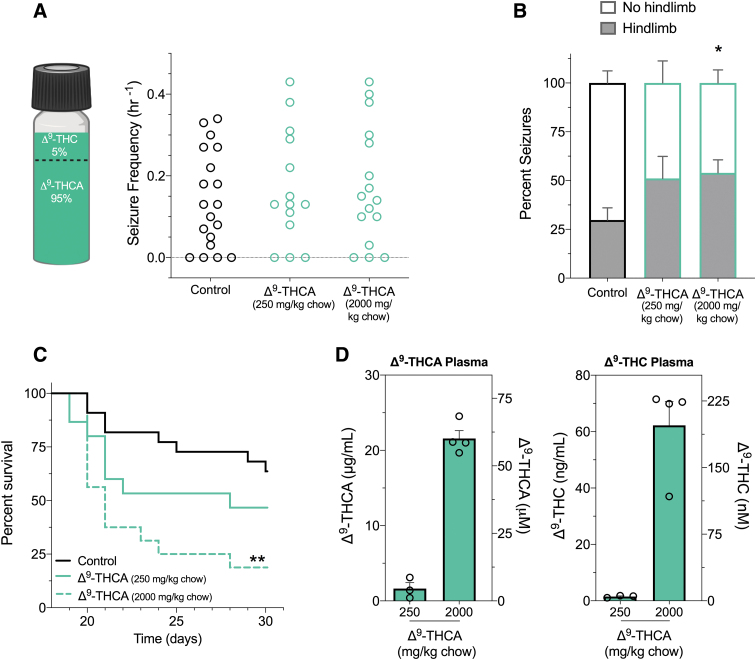
FIG. 5.
The effects of Δ9-THCA on spontaneous seizures and survival in Scn1a+/− mice. (A) A Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture was used for spontaneous seizure and survival experiments in Scn1a+/− mice. Cannabinoid content of the Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture used was 95% Δ9-THCA and 5% Δ9-THC. GTCS frequency of individual untreated and Δ9-THCA-treated mice is given. Treatments were administered orally through supplementation in chow, which was initiated after the induction of a single thermally induced seizure. Unprovoked, spontaneous GTCS were quantified over a 60-h recording period. Treatment with the Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture had no effect on incidence or frequency of seizures, with n=14–19 per group (Fisher's exact text and one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc, respectively). (B) Proportion of spontaneous GTCS with (gray bars) or without (white bars) full tonic hindlimb extension is given. Subchronic treatment with high-dose Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture (2000 mg/kg chow) significantly increased the severity of GTCS in Scn1a+/− mice. The proportion of GTCS with tonic hindlimb extension was significantly greater compared with control-treated mice (*p<0.05; Bonferroni's planned comparisons). Error bars represent SEM with n=11–15. (C) Survival curves comparing control and Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture-treated mice are given. Treatment began at postnatal day 18 (P18) and survival was monitored until P30. Survival of Scn1a+/− mice was significantly worse with high-dose Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture (2000 mg/kg chow), with n=15–22 per group (**p<0.005; log-rank Mantel–Cox). (D) Plasma concentrations of Δ9-THCA (left panel) and Δ9-THC (right panel) from individual experimental animals treated with a Δ9-THCA/Δ9-THC mixture. Concentrations are depicted as both mass concentrations (left y-axis) and molar concentrations (right y-axis). Error bars represent SEM, with n=3–4 per treatment.