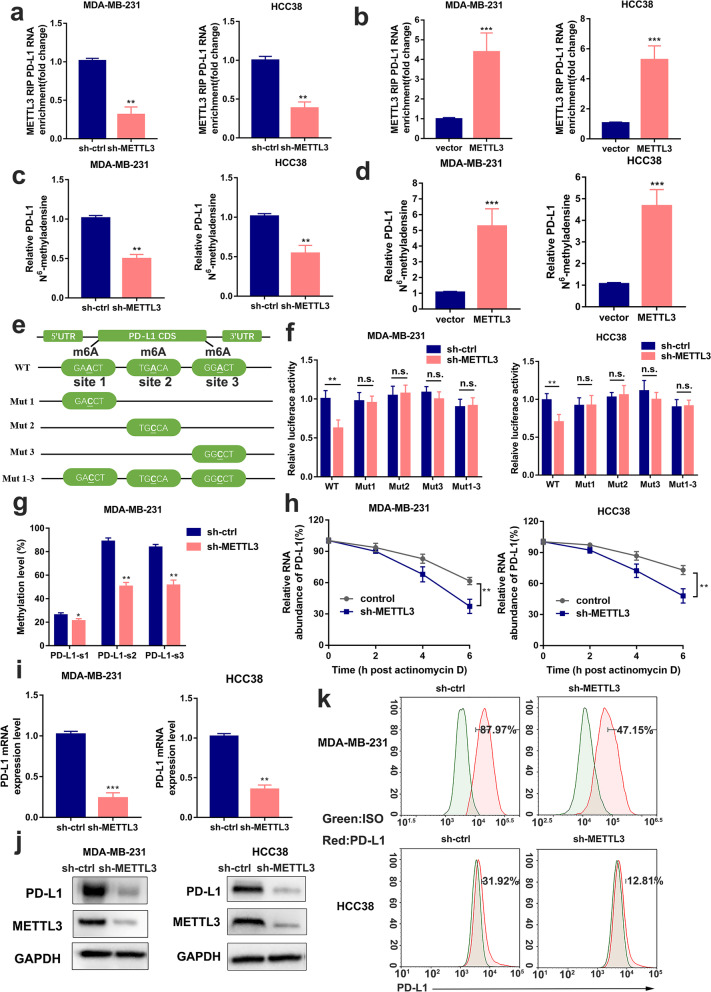
Fig. 2.
METTL3 increases m6A modification and expression of PD-L1 mRNA. a-b The interaction between METTL3 and PD-L1 mRNA was analyzed by RIP-qPCR assay in MDA-MB-231 and HCC38 cells with METTL3 knockdown or overexpression. c-d The relative levels of m6A in PD-L1 were tested by MeRIP-qPCR from MDA-MB-231 and HCC38 cells with overexpression or knockdown of METTL3. e Putative m6A modification sites in the CDS sequence of PD-L1 and synonymous mutations in the PD-L1 CDS. f Relative activity of the WT or Mut luciferase reporters in METTL3-silenced MDA-MB-231 and HCC38 cells was determined (normalized to negative control groups). g The m6A levels of three specific sites of PD-L1 (correspond to the figure e) were determined by absolute quantification of m6A modification. h PD-L1 mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR in MDA-MB-231 and HCC38 cells (control and METTL3 disruption) after actinomycin D treatment (normalized to 0 h). i-k PD-L1 mRNA, protein and cell surface expression levels were detected by qRT-PCR, western blot and flow cytometry in sh-Ctrl or sh-METTL3 MDA-MB-231 and HCC38 cells. Values are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s., no significance