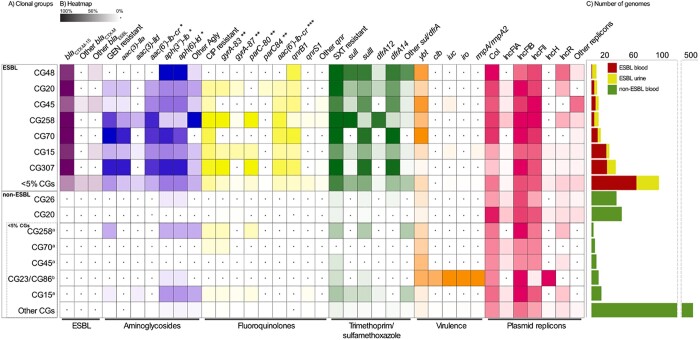
Figure 4.
Distribution of resistance determinants, virulence factors and plasmid replicons among clonal groups (CGs). For data see Table S3. (a) Distribution of CGs in the ESBL and non-ESBL groups, separated by most prevalent CGs (each representing ≥5% of isolates in group) and other CGs. In the non-ESBL group, <5% CGs which were the (i) most prevalent CGs from the ESBL group and the (ii) hypervirulence-associated CG23 and CG86 are shown separately. (b) The intensity of the box shading indicates the percentage of genomes harbouring the respective determinant. White shading with a black dot indicates that there are no determinants present. For each antibiotic class, the presence of resistant phenotype and resistance determinants are indicated. GEN, gentamicin, CIP, ciprofloxacin, SXT, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, Agly, acquired aminoglycoside resistance genes; *, does not confer resistance to gentamicin; **, chromosomal mutation position; ***, may reduce susceptibility to both aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones. (c) Total number of genomes in the ESBL and non-ESBL groups.