Figure 3.
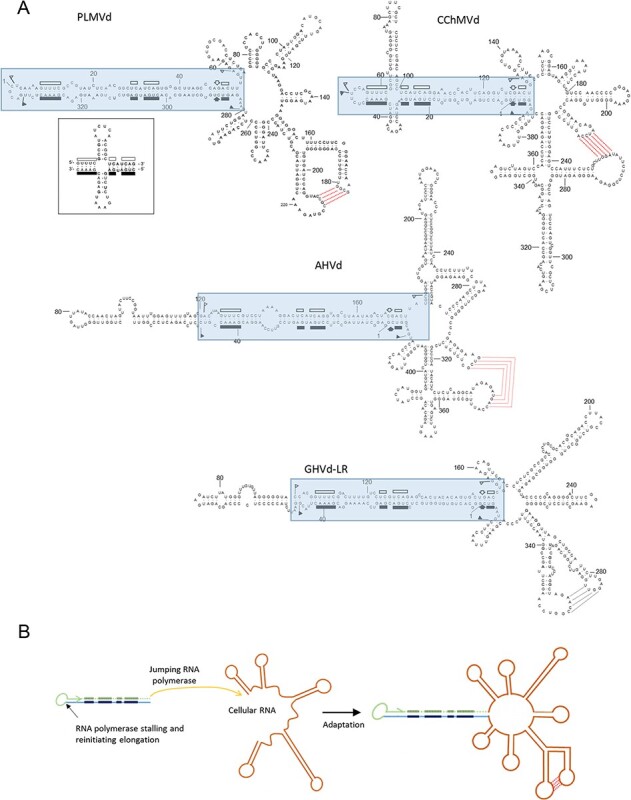
(A) Branched conformation proposed for PLMVd, CChMVd, AHVd, and GHVd-LR. Boxed sequences correspond to the possible replicative module derived from an ancestor protoviroid. Symbols are as reported in the legend to Fig. 2. Inset: alternative cruciform structure of the hammerhead arm proposed for some PLMVd sequence variants. (B) Schematic representation of the origin of an ancestor protoviroid of pelamoviroids from a replicative module containing the HHR: the RNA polymerase stalls at the 3ʹ end of the nascent transcript (light blue line) containing the conserved domains of an HHR (dark blue segments) and reinitiates elongation copying back the nascent transcript up to its 5ʹ terminal (green line). In this protoviroid, likely generated in the RNA word, the final disposition of the conserved hammerhead domains is the same of the current hammerhead arm found in the genome of all pelamoviroids. It is proposed that within the host cell, the polymerase replicating such a protoviroid after stalling at the 3ʹ terminal of the nascent RNA jumped to a host mRNA and reinitiated transcription copying such an RNA. Mutation and adaptation steps would have finally generated the current pelamoviroids adapted to their hosts. This scheme is consistent with the presence of a similar hammerhead arm in all pelamoviroids and with the presence of largely divergent sequences in most of the rest of their genomic RNAs.
