Figure 2.
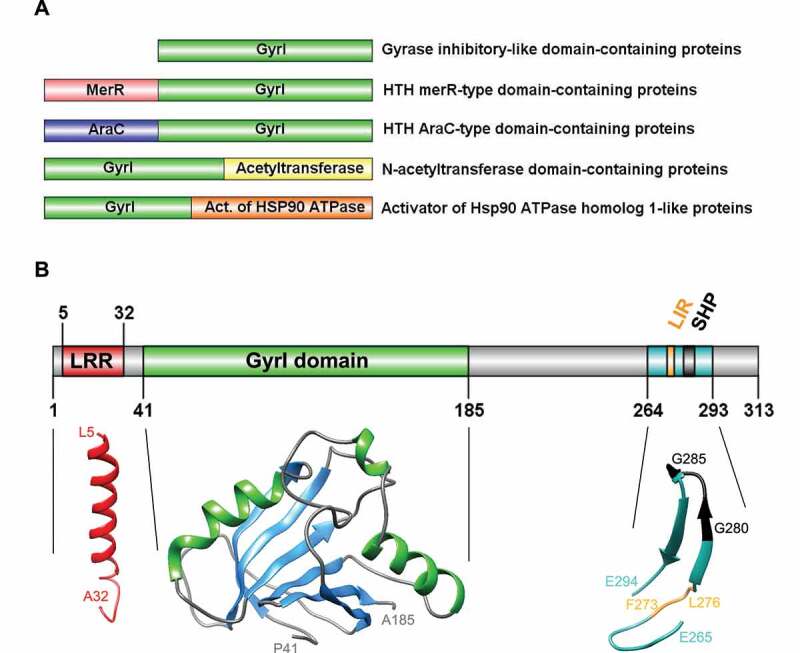
Diversity, topology, and structural models of GyrI proteins. (A) Representative schematics of a subset of GyrI superfamily members, from a total of 73 distinct domain organizations. (B) Topology and structural models of human TEX264 protein motifs and domains. All models were created using the SWISS-MODEL workspace and/or Phyre2 server. GyrI domain was modeled with high to very high confidence based on three templates: SbmC, E. coli Rob transcription factor 2 (1D5Y), and an uncharacterized protein from Chlorobium tepidum (2KCU). The N-terminus of TEX264 bears a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) structural motif that forms an α/β horseshoe fold. The LRR motif was modeled with good to high confidence based on the photosystem II reaction center protein J (6J3Y). The C-terminal part containing the LC3-interacting region (LIR) and VCP-interacting motif (SHP) were modeled with lower confidence based on a Thermotoga maritima mannanase (Man5) carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) (1OF3) and show at least 2 beta-sheets with good model confidence.
