Figure 3.
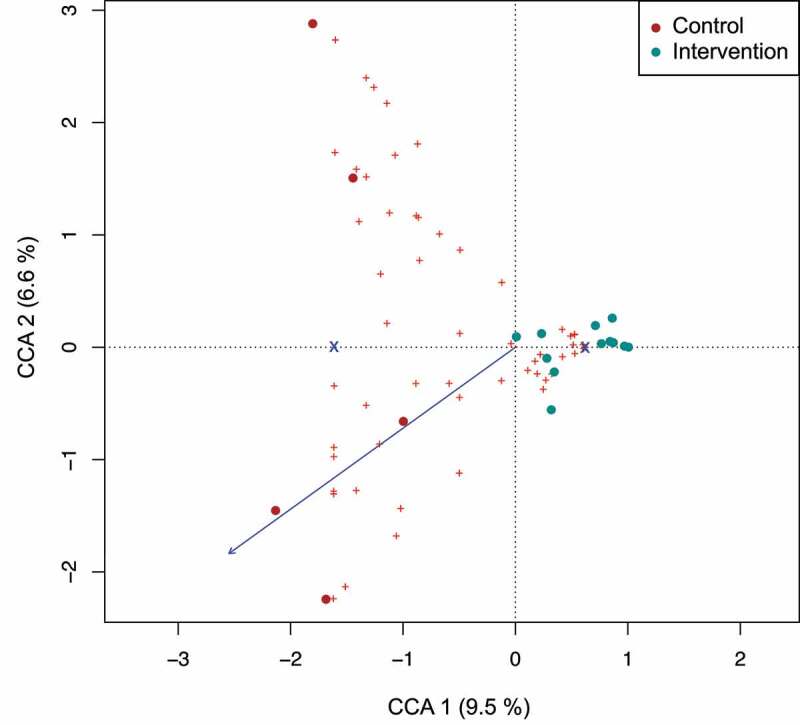
Interdependence of concentration of antibiotics in cord blood with diversity of infant’s gut microbiome in meconium samples. Constrained correspondence analysis with administration of intrapartum antimicrobial prophylaxis set as constrain 1 and concentration of antibiotic in blood as constrain 2 revealed that 6.6% of variation was explained by the concentration of antibiotic in the cord blood suggesting the dependence of changes in microbiome of meconium on the identified concentration of antibiotic.
