FIG 5.
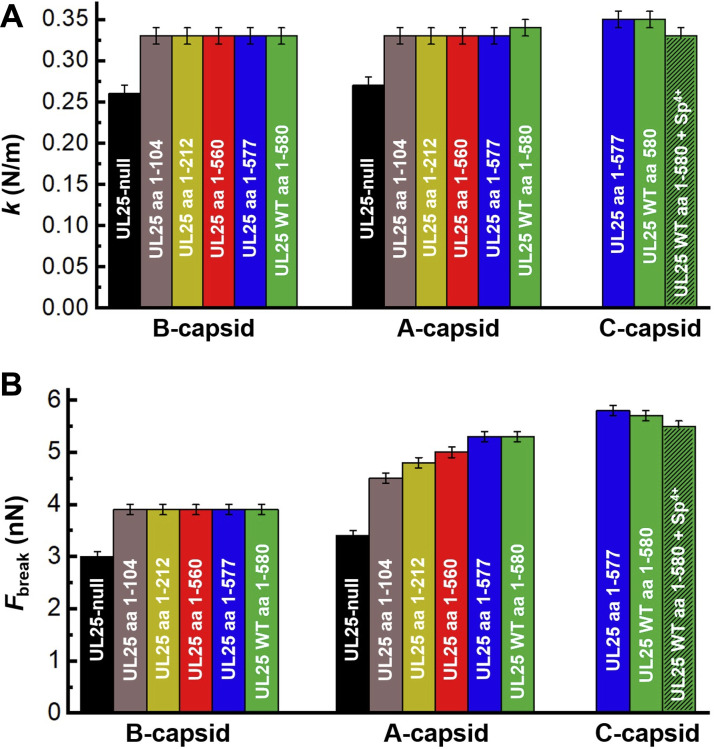
Spring constant, k, (Fig. 4A) and breaking force, Fbreak, (Fig. 4B) reflect the mechanical stability of HSV-1 UL25 mutant capsids as a function of the number of amino acids (aa) in UL25 before the stop codon (s) (WT UL25 has 580 aa). For both B-capsids and A-capsids, spring constant (top) and breaking force (bottom) showed a significant increase when UL25 aa length is increased from aa 0 (UL25-null) to aa 104. For B-capsids, both breaking force and stiffness remain constant when aa length of UL25 is further increased from aa 104 to aa 580. For A-capsids, while the spring constant is unchanged for UL25 mutants with aa 104 to 580, the breaking force continued to rise with increasing aa of UL25 up to aa 577. UL25 aa 1 to 577 mutant had the same capsid stability as WT UL25 capsid with 580 aa UL25.