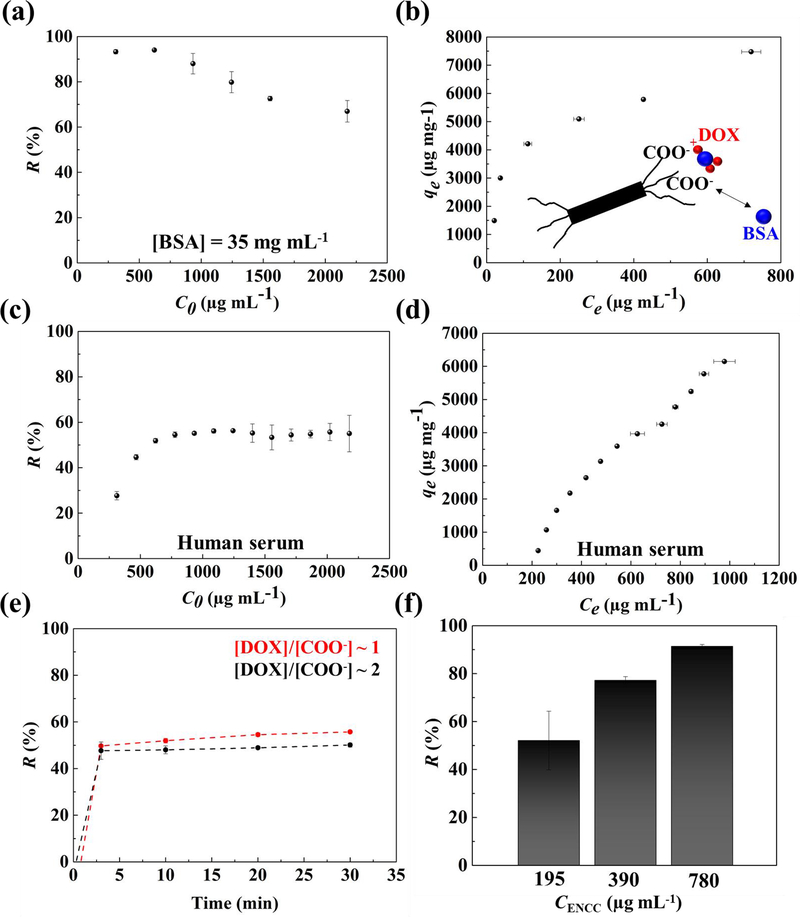
Fig. 4. ENCC-mediated DOX capture in physiological media.
Effect of BSA on the DOX (a) removal percentage and (b) capture capacity of ENCC, showing that the serum albumin not only does not impair the drug capture capability of ENCC, but also enhances the removal capacity as a result of DOX-protein binding. The DOX (c) removal percentage and (d) capture capacity of ENCC in human serum. The DOX capture capacity of ENCC in human serum is remarkably high, possibly as a synergistic effect of drug-protein complex formation. (e) The drug capture time scale in human serum is extremely short, allowing for almost immediate removal of the chemotherapy drug. (f) Increasing the ENCC concentration increases the DOX removal capacity, allowing for almost complete elimination of the drug.