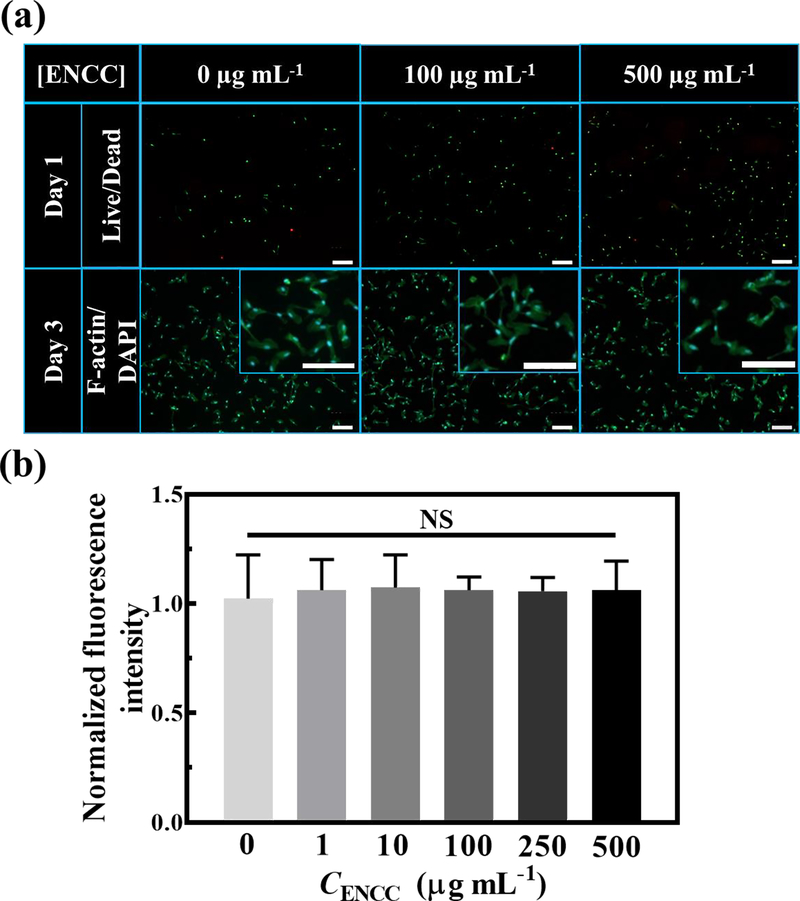
Fig. 5. ENCC cytotoxicity.
(a) Effect of ENCC concentration on the HUVECs, shown with live (green)/dead (red) and F-actin (green)/DAPI (blue) staining after 24 h and 72 h post nanoparticle exposure, respectively. Magnified F-actin/DAPI images are shown in the insets. Almost all the cells are viable and have undergone spreading and elongation with no significant damage to their nuclei. The scale bars are 200 μm. (b) Metabolic activity of HUVECs after 72 h exposure to various concentrations of ENCC normalized with the metabolic activity in the absence of ENCC, obtained using the PrestoBlue™ assay. The unchanged metabolic activity of HUVECs show that ENCC is not toxic against endothelial cells.