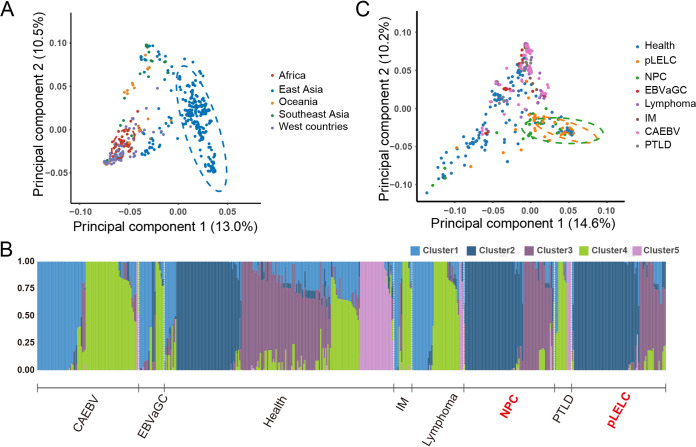
FIG 3.
Principal component and population structure analysis of EBV genome. (A) Principal-component analysis (PCA) of 115 EBV isolates newly assembled in our study and 622 published isolates worldwide. The first two principal-component scores (PC1 and PC2) are indicated in the axes. PC1 explains 13.0% of the total genomic variance, which can clearly distinguish the EBV strains from East Asia. (B) Admixture analysis with 520 EBV isolates derive from East Asia. EBV strains from pLELC (consist of Cluster2/Cluster3-dominated EBV strains) share highest similarity with those from NPC compared with other diseases. (C) PCA of 520 EBV isolates derive from East Asia. CAEBV, chronic active EBV infection; EBVaGC, EBV-associated gastric carcinoma; IM, infectious mononucleosis; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma; PTLD, posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders; pLELC, pulmonary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma.