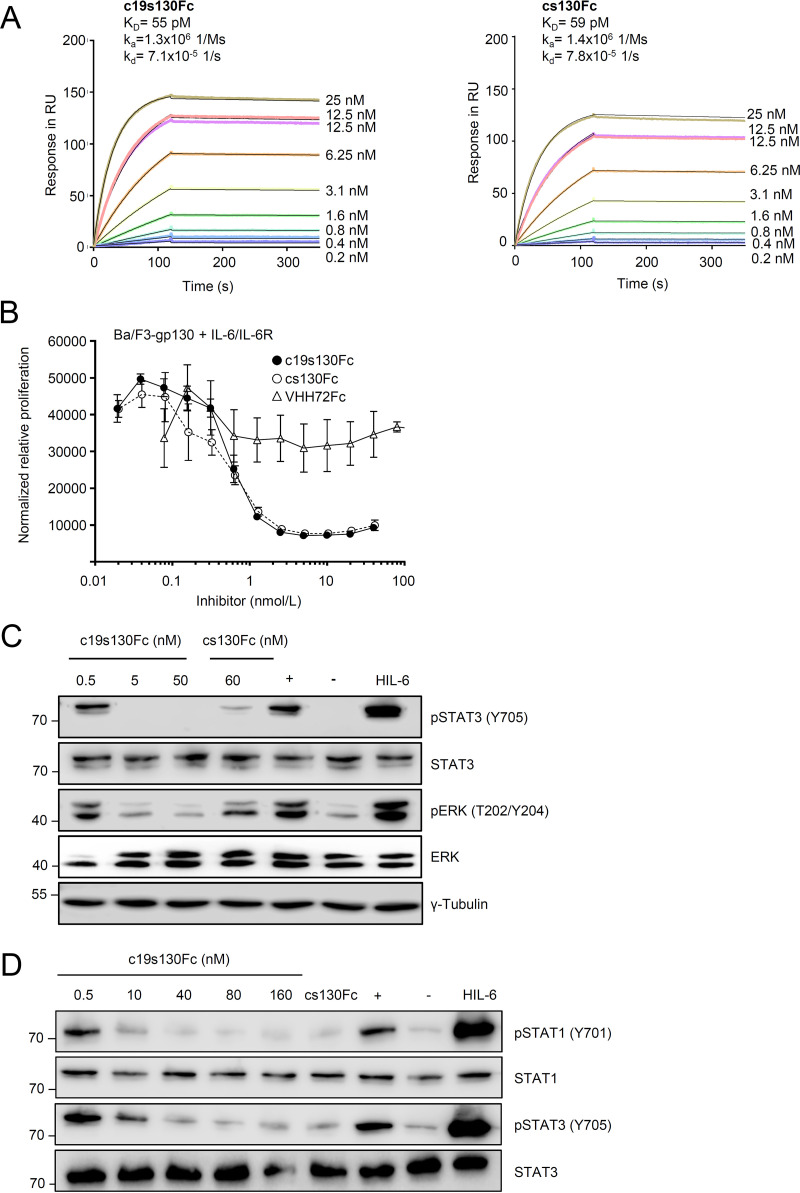
FIG 2.
c19s130Fc blocks IL-6 trans-signaling. (A) SPR analysis of HIL-6 binding to c19s130Fc. c19s130Fc was immobilized on a protein A chip, and increasing concentrations of HIL-6 were injected. Sensorgrams in response units (RU) over time are depicted as colored lines, and global fit data are displayed as black lines. KD, equilibrium dissociation constant; kd, dissociation constant. (B) Ba/F3-gp130 cells were stimulated with 100 ng/mL IL-6 and 200 ng/mL sIL-6R in the presence of increasing c19s130Fc, cs130Fc, or VHH72Fc concentrations. At 72 h poststimulation, cellular proliferation was detected using CellTiter-Blue. Assay results are representative of data from three independent experiments. (C) Western blot analysis of Ba/F3-gp130 cells stimulated for 30 min with 8 nM IL-6 and 1 nM sIL-6R in the presence of the indicated concentrations of c19s130Fc and cs130Fc. Prior to stimulation, IL-6, sIL-6R, and inhibitors were incubated separately for 30 min. Western blots were stained for pSTAT3, STAT3, pERK, and ERK. Western blots are representative of results from three independent experiments. Controls for unstimulated cells (−), cells in the absence of c19s130Fc (+), and stimulation with HIL-6 are included. (D) Western blot analysis of Vero cells stimulated for 30 min with 400 ng/mL IL-6 and 200 ng/mL sIL-6R in the presence of the indicated concentrations of c19s130Fc and cs130Fc. Prior to stimulation, IL-6, sIL-6R, and inhibitors were incubated separately for 30 min. Western blots were stained for pSTAT3, STAT3, pSTAT1, and STAT1. Western blots are representative of results from three independent experiments. Controls for unstimulated cells (−), cells in the absence of c19s130Fc (+), and stimulation with HIL-6 are included.