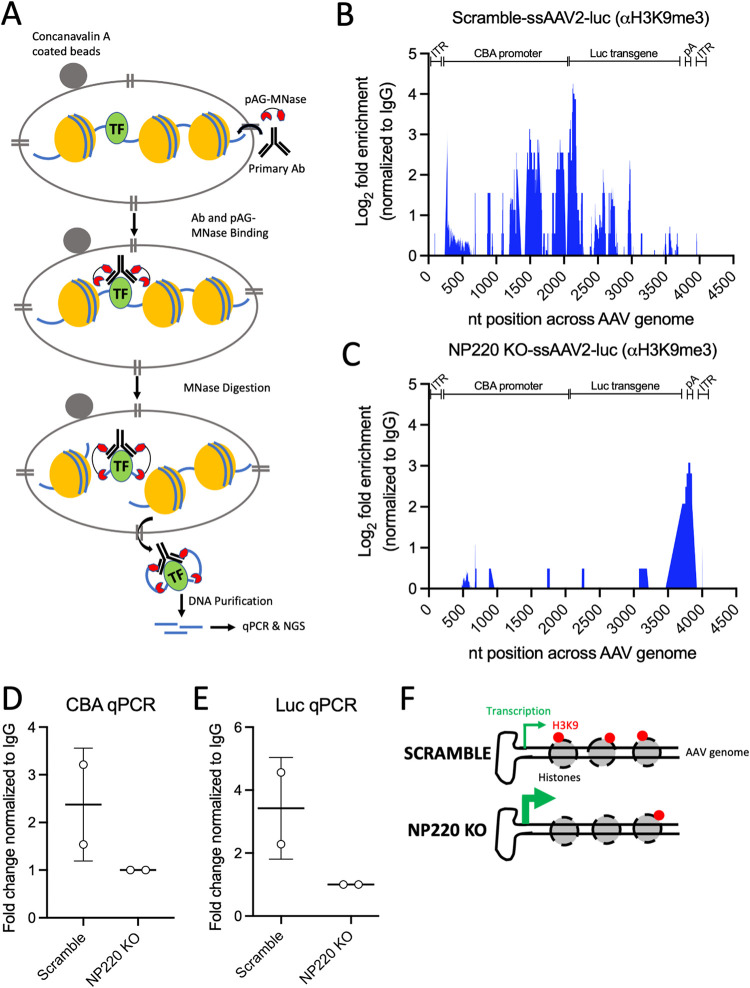
FIG 5.
Epigenetic modification of AAV genomes is regulated by NP220. (A) Schematic of Cut&Run assay, a highly sensitive version of ChIP assay, used here to determine presence of methylation marks on histones bound to the AAV genome. (B and C) Mapping of reads to the AAV genome obtained from next-generation sequencing of Cut&Run assay H3K9me3 immunoprecipitates from HEK293 Scr (B) and NP220 KO cells (C) transduced with ssAAV2-luc at 1,000 vg/cell for 72 h. Percentage of reads mapped to the AAV genome in H3K9me3 antibody pulldown samples were subtracted from matched isotype IgG antibody pulldown samples and expressed as log2 fold enrichment normalized to IgG. (D and E) qPCR quantification of AAV DNA sequences mapping to the peaks observed in panel B. Specific primers targeting regions in the CBA promoter (D) and luciferase transgene (E) were used in the qPCR. Fold change in the threshold cycle (CT) values is normalized to the IgG control. Data shown are from two independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± SD. (F) Schematic depicting the negative regulatory role of NP220 on AAV gene expression. Enhanced transcription of AAV genome is observed in cells lacking NP220 (KO), whereas cells expressing NP220 (Scr) suppress AAV gene expression by depositing repressive H3K9me3 marks across the AAV genome, especially in the promoter and transgene.