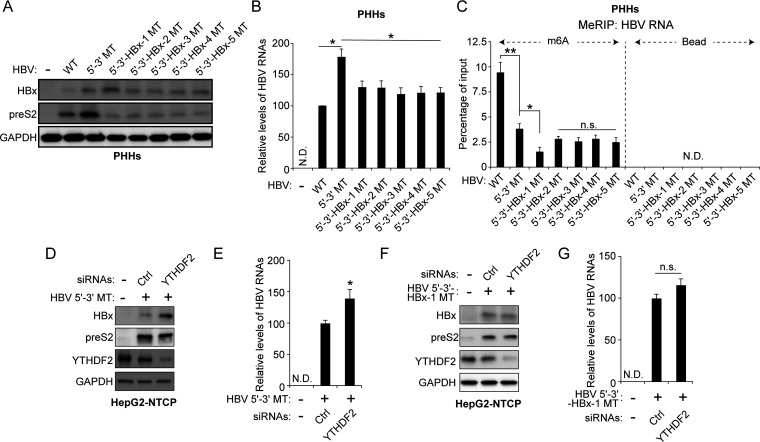
FIG 4.
Regulation of HBx protein by m6A modification in the HBV-infected PHHs and HepG2-NTCP cells. (A to C) HBV particles prepared from the indicated HBV genome-transfected cells were used to infect primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) for 10 days. Total RNA and cellular lysates were extracted from these cells. (A) The indicated proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. (B) HBV RNA levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR. (C) Total RNAs extracted from the cells shown in panel A were immunoprecipitated using an anti-m6A antibody to identify m6A methylated HBV RNAs. These were normalized by input RNA levels by RT-qPCR. (D to G) HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with infectious virus particles prepared from HBV 5′–3′ MT- or 5′–3′-HBx-1 MT-expressing cells for 8 days. HepG2-NTCP cells were also transfected with control and/or YTHDF2 siRNAs for 48 h. Total RNA and cellular lysates were isolated from these cells. (D and F) The indicated proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. (E and G) HBV RNA levels were assayed by RT-qPCR. In panels B, C, E, and G, the error bars represent the SDs from three independent experiments. The P values were calculated via an unpaired Student's t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; n.s., nonsignificant; ND, not detected.