FIGURE 3.
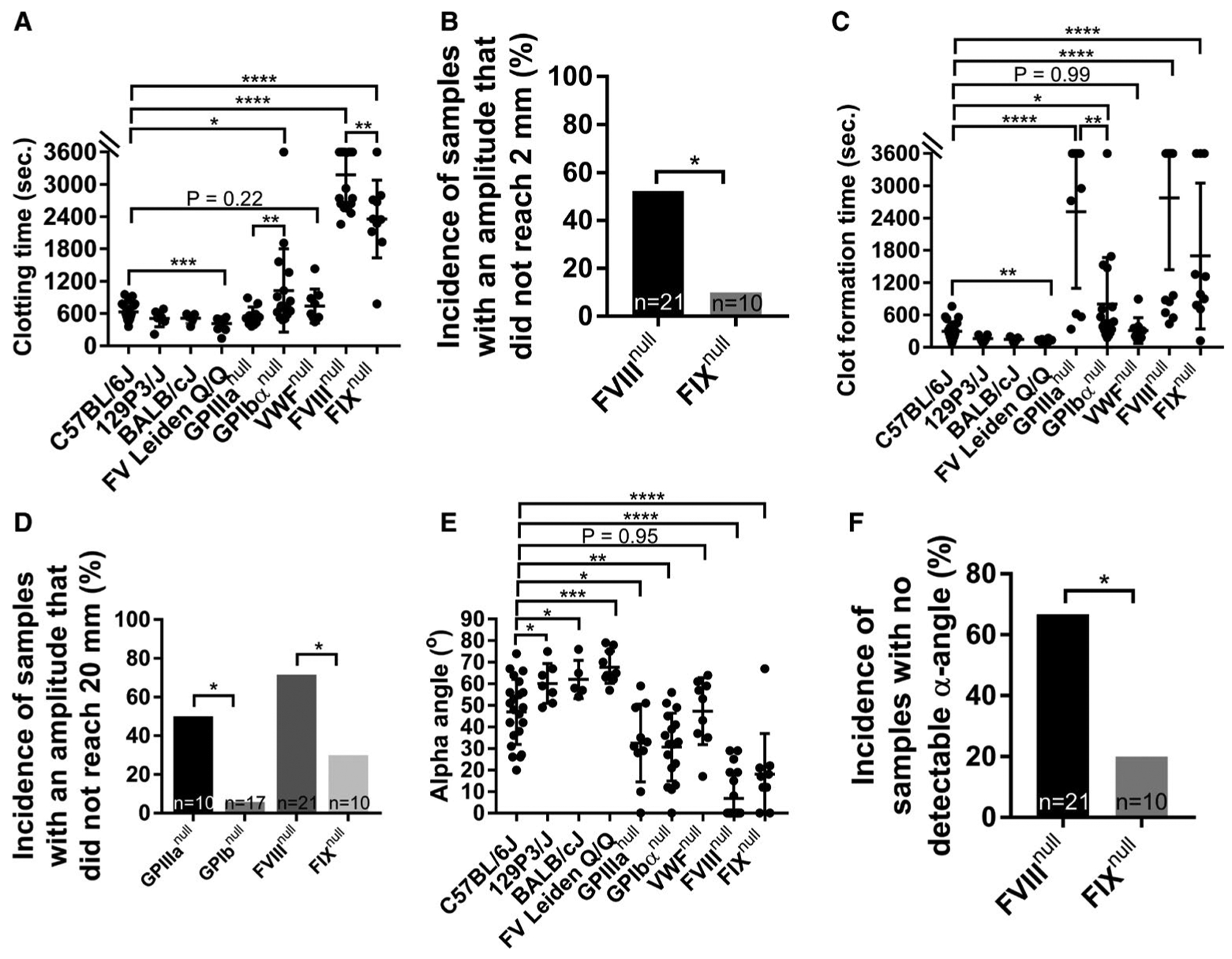
Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) analysis of hemostatic properties in various mouse colonies with bleeding or clotting disorders. Blood samples were collected via inferior vena cava (IVC) blood draw with 3.8% sodium citrate as an anticoagulant (1:10 [vol/vol]). The hemostatic properties of blood samples were determined by ROTEM using the ProCup, in which 21 μl 0.2 M CaCl2 was loaded to the bottom followed by adding 300 μl of citrated blood and parameters were recorded. Samples were run for 1 h. A, Clotting times from various mouse colonies. B, The incidence of samples with an amplitude that did not reach 2 mm, the threshold of clotting time recorded by ROTEM, in whole blood of factor VIII knockout (FVIIInull) and factor IX knockout (FIXnull) mice. C, Clot formation time from various mouse colonies. D, The incidence of samples with an amplitude that reached 2 mm but did not reach a firmness of 20 mm in platelet glycoprotein IIIa knockout (GPIIIanull), platelet glycoprotein Ibα knockout (GPIbαnull), FVIIInull, and FIXnull mice. E, Alpha angle (α-angle). F, Incidence of samples with no detectable α-angle in whole blood of FVIIInull and FIXnull mice within the test period of 1-h. *P < .05. **P < .01. ***P < .001. ****P < .0001
