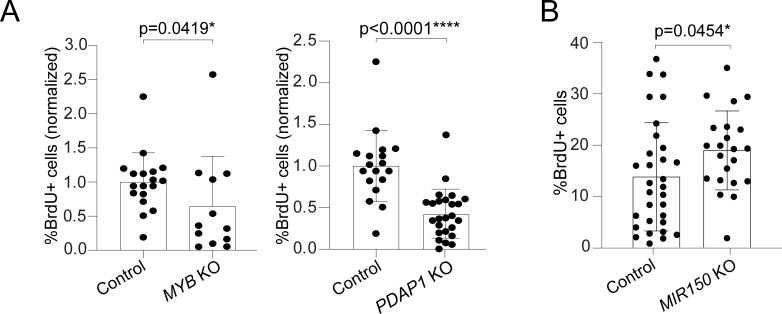
Fig 5. miR-150 restrains T-cell proliferation through MYB and PDAP1.
(A) Primary memory T cells were transfected with Cas-9 RNPs to delete either MYB (left) or PDAP1 (right), followed by single-cell cloning. Individual clones were selected based on the presence of a large genomic deletion in the gene of interest, and proliferation was measured by BrdU incorporation assay. For the MYB gene, N = 18 control clones and N = 12 MYB-edited clones, from 2 independent donors. For the PDAP1 gene, N = 18 control clones and N = 25 PDAP1-edited clones, from 2 independent donors. Mean ± SD. Mann–Whitney test. (B) Memory T cells were transfected with Cas-9 RNP complexes containing 2 different sgRNAs targeting the MIR150 gene. Individual clones were selected based on the presence of a genomic deletion overlapping the MIR150 sequence, and proliferation was measured by BrdU incorporation assay. N = 31 control clones and N = 22 MIR150-edited clones, from 2 independent donors. Mean ± SD. Welch t test, 2 tailed. Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. sgRNA, single-guide RNA; KO, knockout; PDAP1, PDGFA-associated protein 1; RNP, ribonucleoprotein.