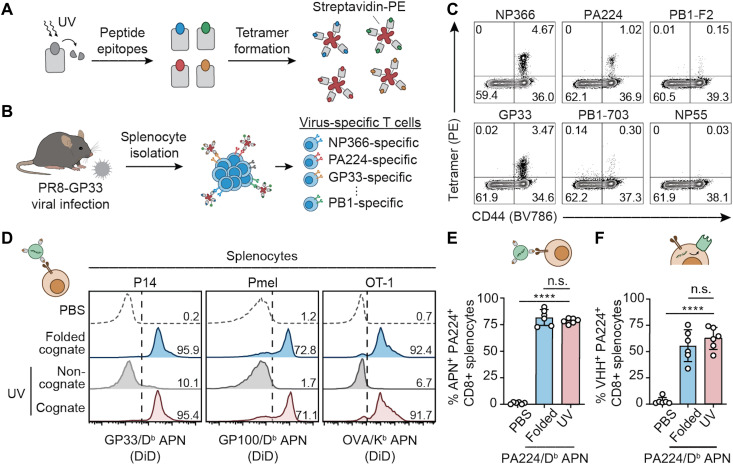
Fig. 4. UV-exchanged APNs transfect Ag-specific T cells equivalently to folded APNs.
(A) Light-triggered peptide exchange technology for high-throughput production of pMHC molecules with various peptide epitopes. pMHC molecules were folded with photolabile peptides that can be cleaved and exchanged with target peptides, followed by tetramer formation with streptavidin conjugated with R-phycoerythrin (PE). (B) Using the UV-exchanged tetramer library to stain virus-specific T cells in a mouse model of PR8-GP33 flu infection. (C) Flow cytometry validation of five epitopes showing diverse Ag specificity of T cell responses to PR8-GP33 flu infection. (D) Equivalent CD8+ splenocyte binding efficiency of UV-exchanged APNs to conventionally folded APNs in three TCR transgenic mouse models in vitro. Numbers indicate the percentage of APN+ cells of CD8+ cells. (E) In vivo targeting activity of UV-exchanged PA224/Db APNs and folded PA224/Db APNs to PA224-specific CD8+ T cells in a mouse model of PR8 infection. n.s., not significant, where P = 0.4548 between folded and UV-exchanged PA224/Db APNs; ****P < 0.0001 between PBS and UV-exchanged PA224/Db APNs; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey post-test and correction. (F) In vivo transfection efficiency of UV-exchanged PA224/Db APNs and folded PA224/Db APNs to PA224-specific CD8+ T cells in a mouse model of PR8 infection. n.s., not significant, where P = 0.5191 between folded and UV-exchanged PA224/Db APNs; ****P < 0.0001 between PBS and UV-exchanged PA224/Db APNs; one-way ANOVA and Tukey post-test and correction. For (E) and (F), all data are means ± SD; n = 6 biologically independent mice.