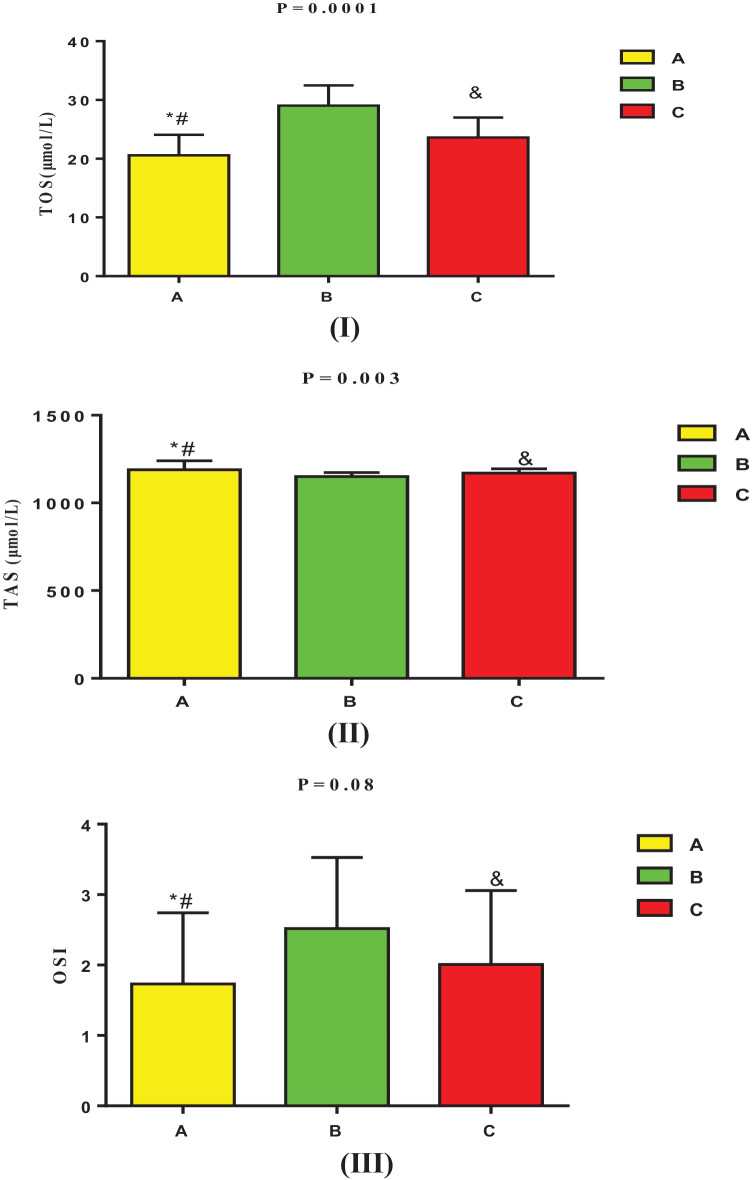
Fig. 3.
Oxidative statue in Covid-19 regarding the effect of allopurinol treatment at time of discharge: (I): total oxidant status (TOS) was lower in mild-moderate Covid-19 patients as compared with severely Covid-19 patients on standard treatment alone (*P = 0.0001 and #P = 0.0008) as compared with severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment plus allopurinol. TOS was lower in severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment plus allopurinol than severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment alone (&P = 0.0001). (II): Total antioxidant status (TAS) was higher in mild-moderate Covid-19 patients as compared with severely Covid-19 patients on standard treatment alone (*P = 0.002), and not significant (#P = 0.87) as compared with severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment plus allopurinol. TAS was higher in severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment plus allopurinol than severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment alone but was not significant (&P = 0.09). (III): Oxidative stress index (OSI) was lower but insignificant in mild-moderate Covid-19 patients as compared with severely Covid-19 patients on standard treatment alone (*P = 0.07), but not significant as compared with severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment plus allopurinol (#P = 0.08). OSI was lower in severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment plus allopurinol than severely affected Covid-19 patients on standard treatment alone, but was insignificant (&P = 0.09).