Extended Data Fig. 1 |. Quality control and extended characterization of cell states identified by unsupervised clustering of scRNA-seq data.
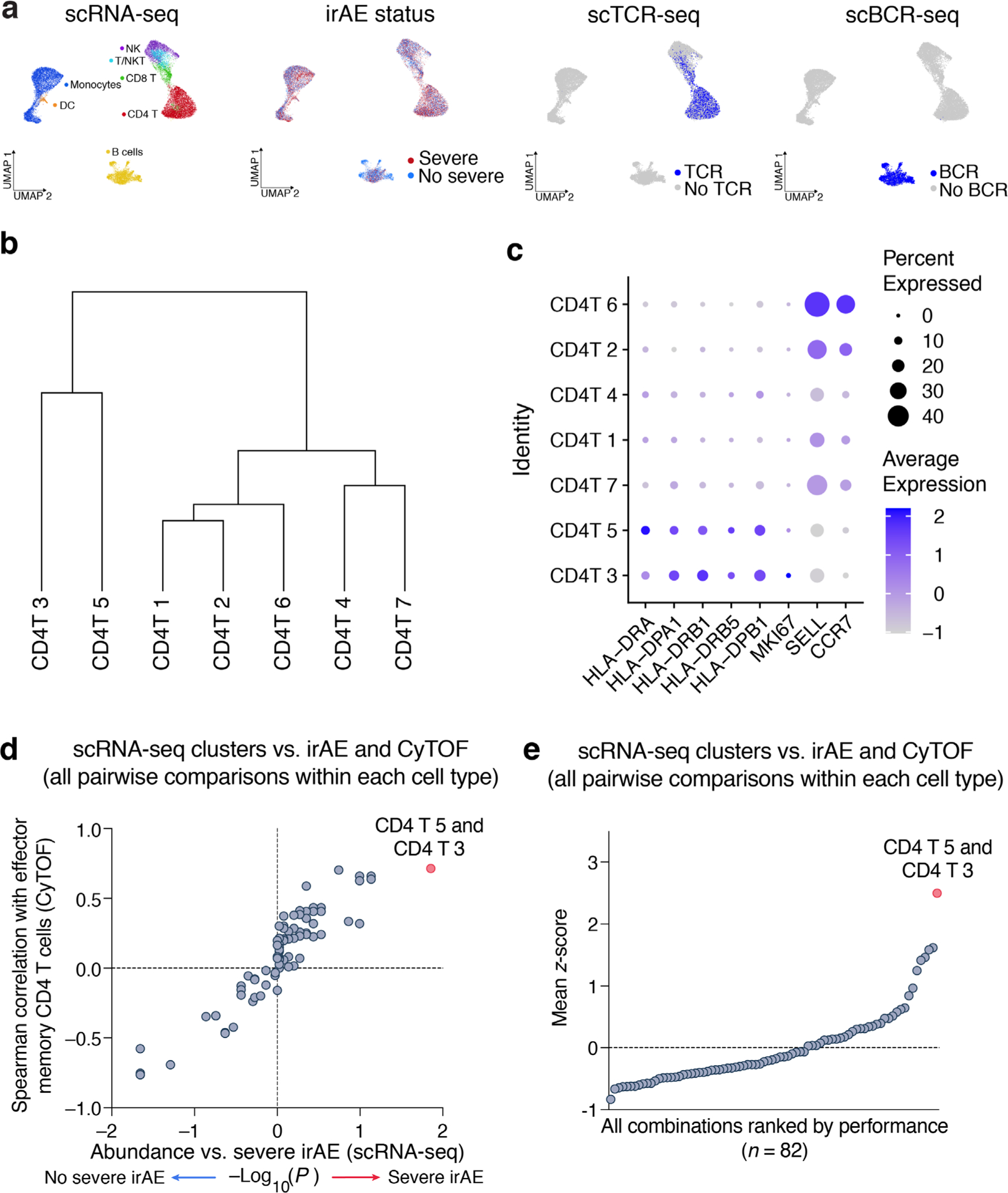
a, UMAP representation of pretreatment peripheral blood leukocytes profiled by droplet-based scRNA-seq (10x Genomics) from 13 patients with metastatic melanoma, colored by major cell lineages, severe irAE status, TCR expression by scV(D)J-seq, and BCR expression by scV(D)J-seq (related to Fig. 3a). b, Unsupervised hierarchical clustering (average linkage) of the mean log2 transcriptome per CD4 T cell cluster identified from scRNA-seq data. c, Dot plot showing the average expression of key activation (HLA-DX, MKI67) and lineage markers (SELL, CCR7) in CD4 T cell clusters. d, Same as Fig. 3b but showing all pairwise combinations of scRNA-seq clusters within each of the major cell types analyzed (B cells, CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, NK cells, monocytes). Across 82 possible pairwise combinations, CD4 T 5 + 3 achieved the highest Spearman correlation against CD4 TEM levels enumerated by CyTOF and the strongest association with severe irAE development. Cells annotated as ‘T/NKT’ were collapsed into CD8 T cells. e, Same as panel d but showing all pairwise combinations ranked by the mean of each feature following unit variance normalization (mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1). In this analysis, the −log10 P-value for the association with severe irAE (two-sided, unpaired Wilcoxon rank sum test) was normalized to unit variance without considering the direction of the association.
