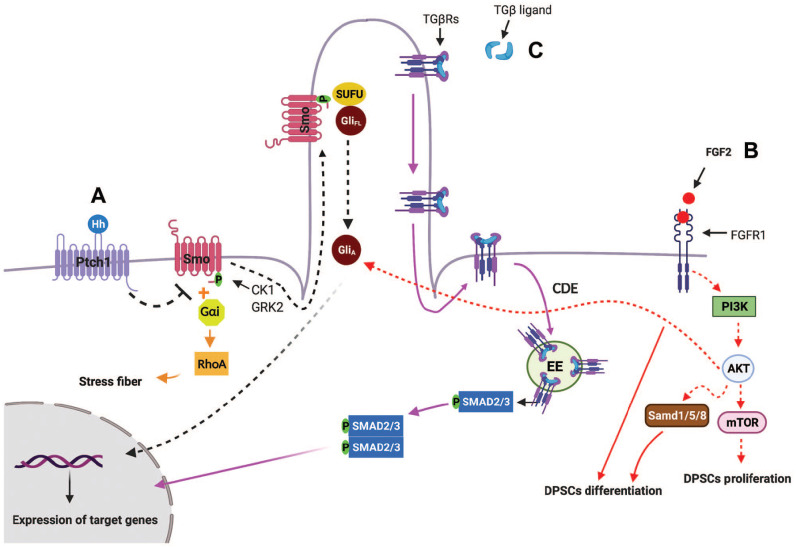
Figure 2.
Schematic and simplified representation of primary cilia-mediated HH, TGF-β, PDGFRα, and FGF signaling pathways. Hedgehog (Hh) signaling. (A) 1. Canonical Hh pathway. In the absence of Hh, Ptch1 prevents the ciliary localization and activation of SMO. When Hh ligand binds to Ptch1, Smo phosphorylates by casein kinase 1 (CK1) and G protein–coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) and moves into primary cilia. Sufu-Gli full length (GliFL) also accumulate in primary cilia, where Smo disassociates Sufu-GliFL, resulting in activation of Gli (GliA). GliA then translocases into nucleus and induces the expression of Hh target genes (black arrows). 2. Noncanonical Hh pathway. One of the noncanonical Hh signaling that is independent of primary cilia is Hh-RhoA signaling, in which Smo-coupled with Gαi proteins activates small GTPase RhoA, which regulates actin stress fiber (orange arrows). (B) Crosstalk among primary cilia, FGF2-FGFR1, Hh, and PI3K-AKT signaling: binding of FGF2 ligands to FGFR1 activates PI3K-AKT-mTOR, resulting in dental pulp stem cell (DPSC) proliferation. In addition, FGF2/FGFR1 activate BMP2 signaling and also induce AKT activation, which aid Hh signaling, resulting in DPSC differentiation (red arrows). (C) TGF-β signaling: in the presence of TGF-β, TGβR I and II translocate from the ciliary membrane to the ciliary pocket through the clathrin-dependent endocytosis (CDE) process, which will result in phosphorylation of SMAD transcription factors 2/3 (SMAD2/3) in early endosomes (EEs) at the ciliary base. Then, the SMAD2/3 complex translocates into the nucleus and activates transcription of TGF-β target genes (purple arrows).