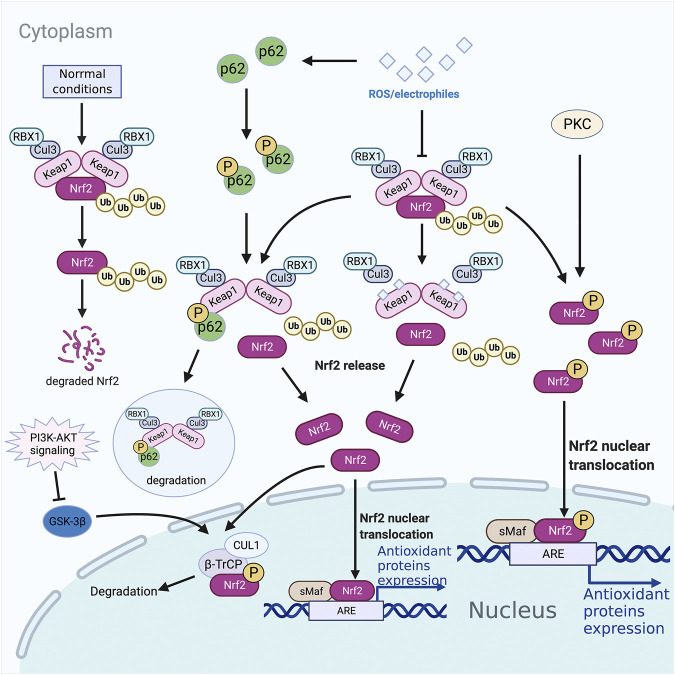
FIGURE 1.
Nrf2 associated pathways. Proteases degrade nrf2 ubiquitinated by the Keap1-CUL3 complex under normal conditions in the cytoplasm. However, under oxidative stress conditions, Nrf2 dissociates from Keap1, accumulates in the cytoplasm, and is transported into the nucleus to bind to target genes. The selective autophagy substrate p62 could compete with Nrf2 for Keap1 binding at the bottom of the DC domain, dislocating Nrf2 from Keap1 and leading to the accumulation of Nrf2, initiating the transcription of antioxidant protective genes and phase II detoxification enzyme genes. PKC phosphorylates Ser40 in Neh2, dissociating the Keap1 homodimer, and transporting Nrf2 into the nucleus to recognize and bind the ARE. Neh6 in Nrf2 can be phosphorylated by GSK-3β, leading to degradation through being recognized by β-TrCP. PI3K-AKT signaling could inhibit GSK-3β through phosphorylation. ARE, antioxidant responsive element; β-TrCP, β-transducin repeats-containing protein; GSK-3, phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase 3; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; Nrf2, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; sMAF, small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homologue.