FIGURE 5.
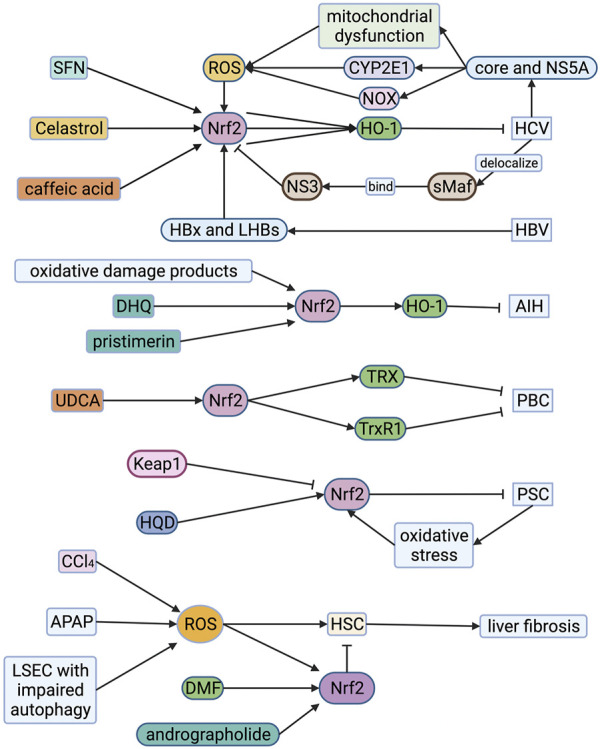
Roles of Nrf2 in viral hepatitis, autoimmune liver disease and liver fibrosis. HCV core protein and NS5A protein induce mitochondrial dysfunction, CYP2E1 and NOX expression in hepatocytes producing large amounts of ROS. HCV core protein and NS5A protein also induce Nrf2 phosphorylation, resulting in up-regulation of HO-1 and NQO1 which alleviate HCV. However, HCV could cause sMAF to delocalize and connect with extranuclear NS3, and then bind to Nrf2 in the cytoplasm, preventing Nrf2 from entering the nucleus. SFN, celastrol and caffeic acid can up-regulate the expression of HO-1 through the Nrf2-associated pathway to inhibit HCV viral replication. The HBx protein of HBV can induce intense stimulation of Nrf2. At the same time, HBV enhances the reciprocity between p62 and Keap1, forming a HBx-p62-Keap1 complex in the cytoplasm, prompting the dissociation of Keap1-Nrf2, which contributes to activation of Nrf2. Oxidative damage products, dihydroquercetin (DHQ) and pristimerin increase the expression of Nrf2 in the cytoplasm, significantly enhancing the transcriptional expression of the HO-1 alleviating AIH. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) enhances the activation of Nrf2 in liver cells of PBC patients, increasing TRX and TrxR1 protein which alleviate PBC. Huangqi Decoction (HQD) up-regulates the expression of Nrf2 for alleviating PSC. ROS is one of the activating factors of hepatic stellate cells (HSC). It also promotes the activation of Nrf2 which suppresses HSC. Andrographolide and dimethyl fumarate (DMF) can significantly ameliorate the stimulation of HSC by enhancing Nrf2 and increasing the expression of antioxidant proteins. The damage of sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSEC) during acute liver injury can aggravate the oxidative stress response and activate HSC to promote liver fibrosis. The increase of p62 level caused by impaired autophagy will trigger the stimulation of Nrf2 and the up-regulation of its target gene, alleviating liver fibrosis. AIH, autoimmune hepatitis; APAP, acetaminophen; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; CYP2E1, cytochrome P450 2E1; DHQ, dihydroquercetin; DMF, dimethyl fumarate; HO-1, hemeoxygenase-1; HQD, Huangqi Decoction; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; Nrf2, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; NOX, NADPH oxidase; PBC, primary biliary cholangitis; PSC, primary sclerosing cholangitis; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SFN, sulforaphane; sMAF, small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homologue; TRX, thioredoxin; TrxR1, thioredoxin reductase 1; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid.
