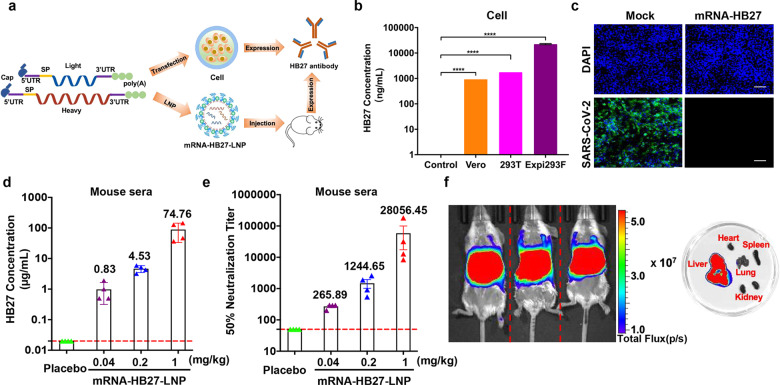
Fig. 1. Rational design and characterization of the mRNA antibody.
a Design and encapsulation of an mRNA antibody mRNA-HB27-LNP. b HB27 antibody expression in Vero, 293 T and Expi293F cells at 24 h after transfection with mRNA-HB27 using ELISA assay. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Data are analyzed by One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons (****P < 0.0001). c Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Vero cells at 24 h after transfection with 1 μg of mRNA-HB27 by Immunofluorescence assay. SARS-CoV-2 S protein was stained in green, and DAPI in blue. Scale bars, 100 μm. d, e The antibody concentration and NT50 titer of serum samples in mice. Briefly, female BALB/c mice (n = 4/group) were i.v. administrated with the indicated dose of mRNA-HB27-LNP or Placebo. Then, mice sera at 24 h post administration were measured by ELISA (d) and SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization assay (e), respectively. Dotted lines indicate the limits of detection. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. f Intravenous injection of reporter mRNA-LNPs for in vivo imaging in mice. IVIS Spectrum image (6 h post-injection) of female BALB/c mice were injected with 10 μg of FLuc-encoding reporter mRNA-LNP by the intravenous route.