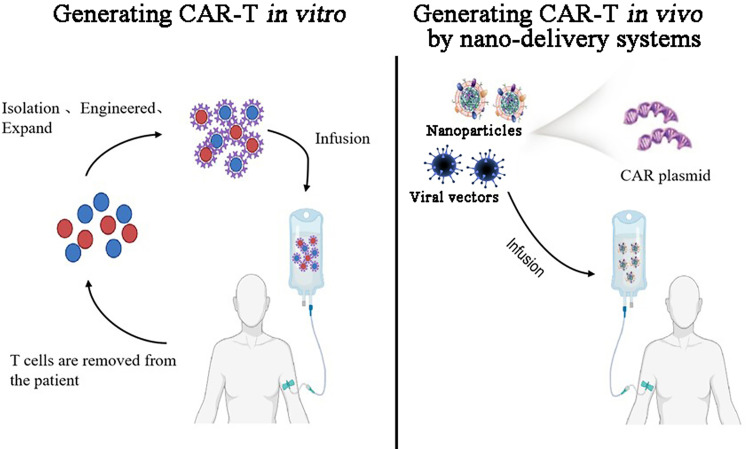
Figure 5.
Comparison of generating CAR-T in-vitro and generating CAR-T-in-vivo by nano-delivery systems: In-vitro CAR T cells are first isolated from the patient, proliferated in-vitro, and then genetically engineered to screen the successfully edited CAR T cells, which are amplified to a certain number of infusions into the patient. In-vivo induced CAR T cells use nanotechnology to encapsulate CAR-expressing plasmids into nano-delivery systems including polymer nanoparticles and viral vectors such as lentivirus and AAV, which are then targeted to tumor regions in-vivo to edit T cells in-situ at tumor sites to kill tumors.