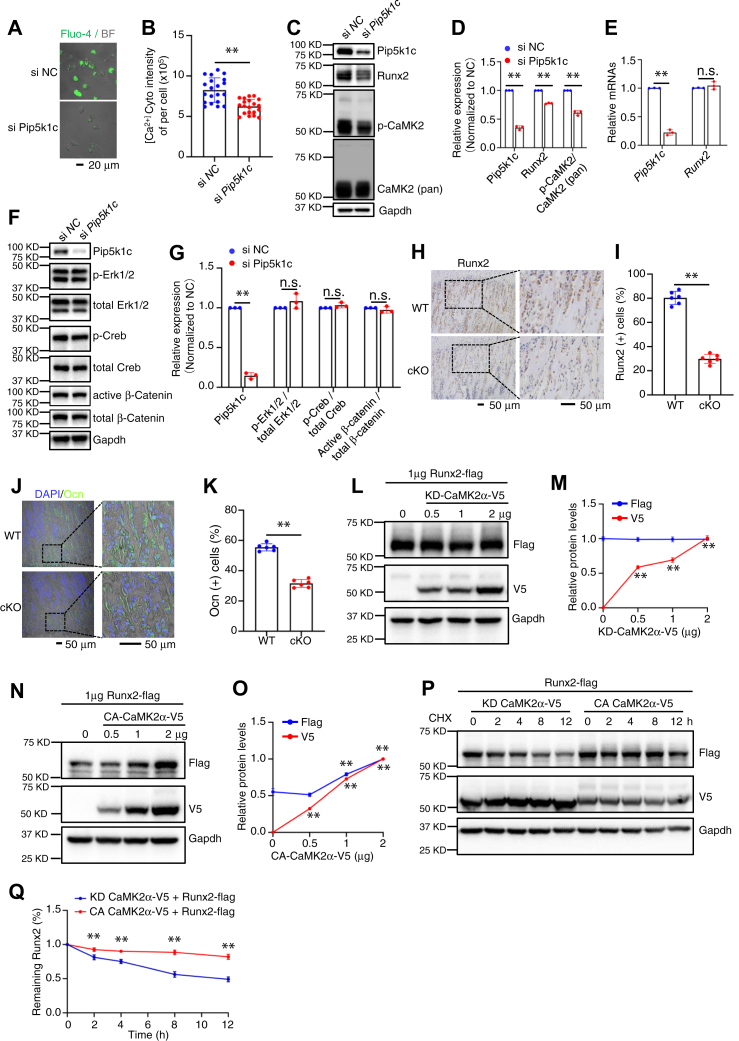
Figure 5.
Pip5k1c regulates Runx2 expression through CaMK2 in BMSC.A and B, Cytosol Ca2+ assay. Primary BMSCs isolated from 4-month-old male mice were plated in confocal dish and knockdown (KD) of Pip5k1c by RNA interference for 48 h. Cells were then applied for Fluo-4/AM staining and signals were collected as described in Methods (A). Scale bar, 20 μm. The total fluorescence intensity was used as the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentrations (B). Results were expressed as mean ± SD; N = 20 cells per group were analyzed. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus si-NC; unpaired two-tailed t test. C–E, primary BMSCs isolated from 4-months-old male mice were seeded in 6-well plate at 4 × 105 cells per well. Pip5k1c was knocked down by RNA interference for 48 h. Protein extracts isolated from the cells were subjected to western blotting with the indicated antibodies (C and D) or RT-qPCR analysis for expression of Pip5k1c and Runx2 mRNAs (E). Gapdh protein and mRNA were used as internal controls for Western blotting and RT-qPCR analysis, respectively. Results were expressed as mean ± SD; N = 3 biologically independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus si-NC; unpaired two-tailed t test. F and G, primary BMSCs isolated from 4-months-old male mice were seeded in 6-well plate at 4 × 105 cells per well. Pip5k1c was knocked down by RNA interference for 48 h. Protein extracts isolated from the cells were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies (F). Gapdh protein were used as internal controls for western blotting analysis. Quantification results (G) were expressed as mean ± SD; N = 3 biologically independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus si NC; unpaired two-tailed t test. H, IHC staining. Tibial sections of control and cKO mice were subjected to IHC staining for expression of Runx2. Scale bar, 50 μm. I, quantification of (H). Results were expressed as mean ± SD; N = 6 mice per group were analyzed. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus control; unpaired two-tailed t test. J and K, tibial sections of control and cKO mice were subjected to IF staining for expression of Osx (J). Scale bar, 50 μm. (K) quantification of (J). Results were expressed as mean ± SD; N = 6 mice per group were analyzed. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus control; unpaired two-tailed t test. L–O, Flag-Runx2 plasmid (1 μg) was transfected into COS-7 cells together with increasing amounts of plasmids expressing a kinase-dead CaMK2α-V5 (KD-CaMK2α-V5) (L and M) or constitutively active CaMK2α-V5 (CA-CaMK2α-V5) (N and O) plasmid. Runx2 expression was determined by Western blotting with anti-Flag antibody at 24 h after transfection. Results were expressed as mean ± SD; N = 3 biologically independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus 2 μg; unpaired two-tailed t test. P and Q, cycloheximide experiments. Flad-Runx2 plasmid was transfected into COS-7 cells together with KD-CaMK2α-V5 or CA-CaMK2α-V5 plasmid. At 24 h after transfection, cells were treated with CHX at 100 μg/ml for the indicated times. Quantification of levels of Runx2 protein was performed (Q). Results were expressed as mean ± SD; N = 3 biologically independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus control; unpaired two-tailed t test. si-NC, control siRNA; CA-CaMK2α, constitutively active form of CaMK2α; CHX, cycloheximide; BMSCs, bone marrow stromal cells; IHC, immunohistochemical.