Figure 1.
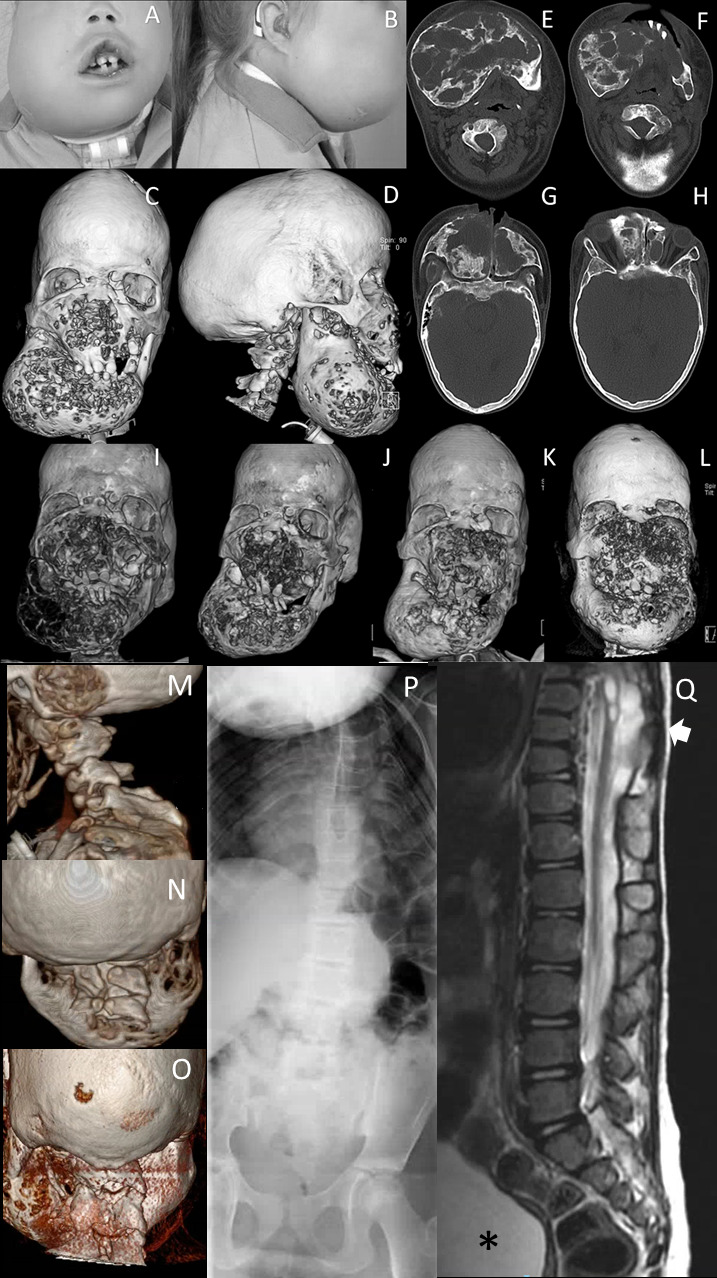
Clinical and radiological facial features of subject 1. (A, B) Facial photographs at age 11. Dysmorphic features include frontal bossing, dolichocephaly, hypertelorism, half-closed eyes, a broad and flat nasal bridge, and an asymmetric bilateral swelling at mandibular and mid-facial levels. (C, D) 3-D reconstructed CT images of the face at age 11 years show a bilateral asymmetric cystic expansion of the mandible, maxilla, ethmoid and frontal bones with medial displacement of the teeth at mandibular level. In addition, frontal bossing and dolichocephaly can be noted. (E–H) Transverse CT images of at mandibular and mid-facial levels at age 11 years show extensive osteolytic and osteoblastic lesions. Note that the lesions are not only at mandibular level but also on mid-facial level and the anterior side of the foramen magnum. (I) 3-D reconstructed CT image of the face at age 9 years shows a bilateral asymmetric cystic expansion of the mandible, maxilla, ethmoid and frontal bones with medial displacement of the teeth and bilateral orbital involvement. (J) One year after the start of pamidronate (age 11 years), small cystic lesions can be seen at mandibular and mid-facial level; note the difference in osseous tissue compared with the CT scan before the start of the therapy. (K) Five years after the start of therapy (age 14 years), more remodelling of osseous tissue has occurred, although small cystic lesions are present. (L) One year after stopping pamidronate and 2 years after shaving approximately 2.5 cm of the right maxilla (age 17 years), multiple cystic lesions at mandibular and mid-facial levels with intensive displacement of the orbita. CT 3-D reconstruction of the skull, with (M) a sagittal view and (N) a posterior view of the cervical spine showing, besides lytic lesions, abnormalities of the cervical vertebrae at the age of 6 years and (O) at 18 years. (P) Spine X-rays at the age of 7 years showing scoliosis and abnormal thoracic vertebrae. (Q) Sagittal T2-weighted MRI of the thoracolumbal spine showing the thoracic syrinx and meningomyelocele (arrow) and neurogenic bladder (asterisk).
