Figure 1. RAS-NF1 interactions are hypothesized to broadly determine whether a RAS mutant CRC is sensitive to EGFR inhibition.
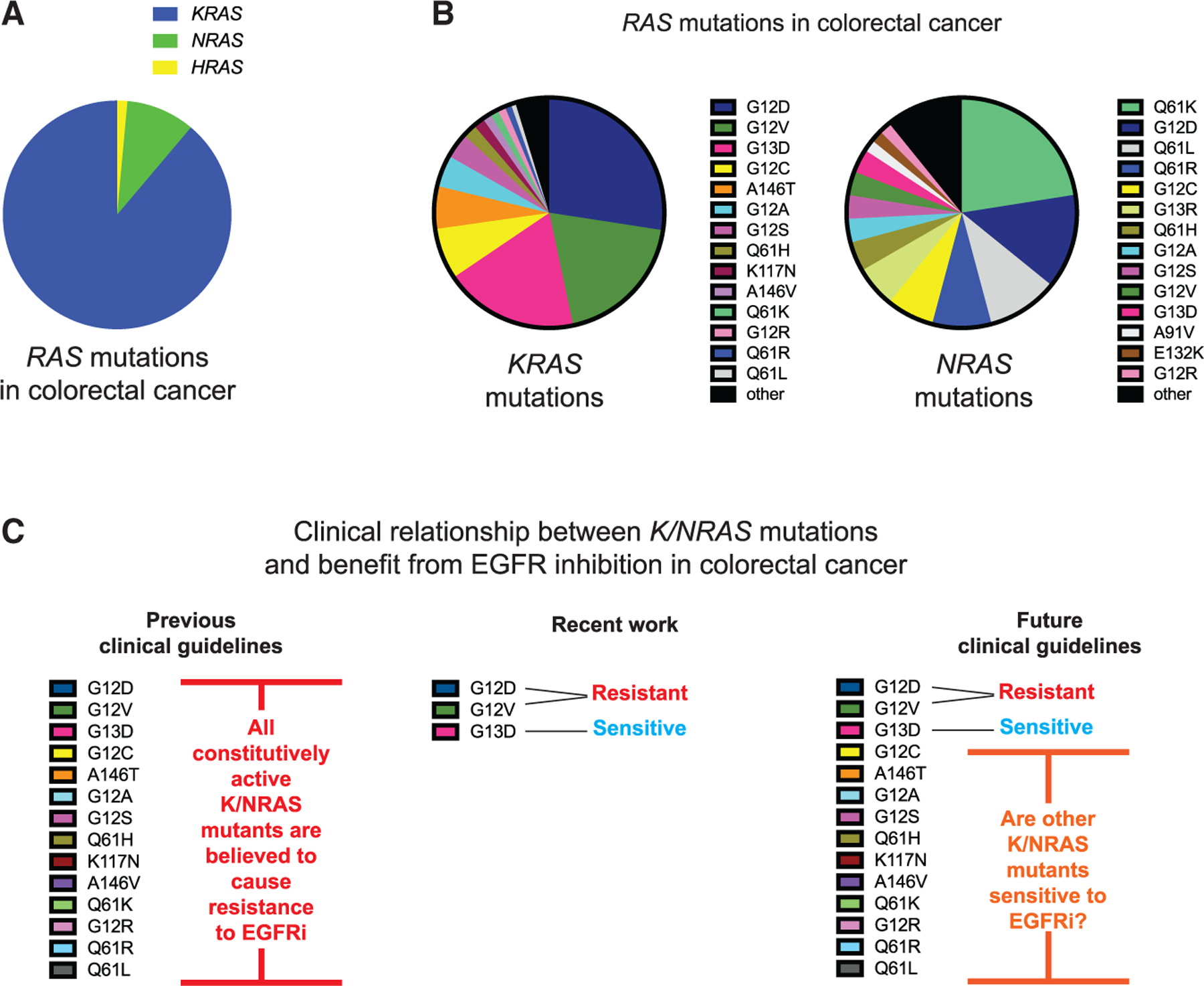
(A) The distribution of RAS mutations between KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS within CRC.
(B) The different KRAS and NRAS mutations that have been observed in CRC.
(C) The establishment of KRAS G13D as an EGFR inhibitor-sensitive mutation necessitates the determination of whether patients with other KRAS and NRAS mutations may also benefit from treatment with EGFR inhibitors (EGFRi)
