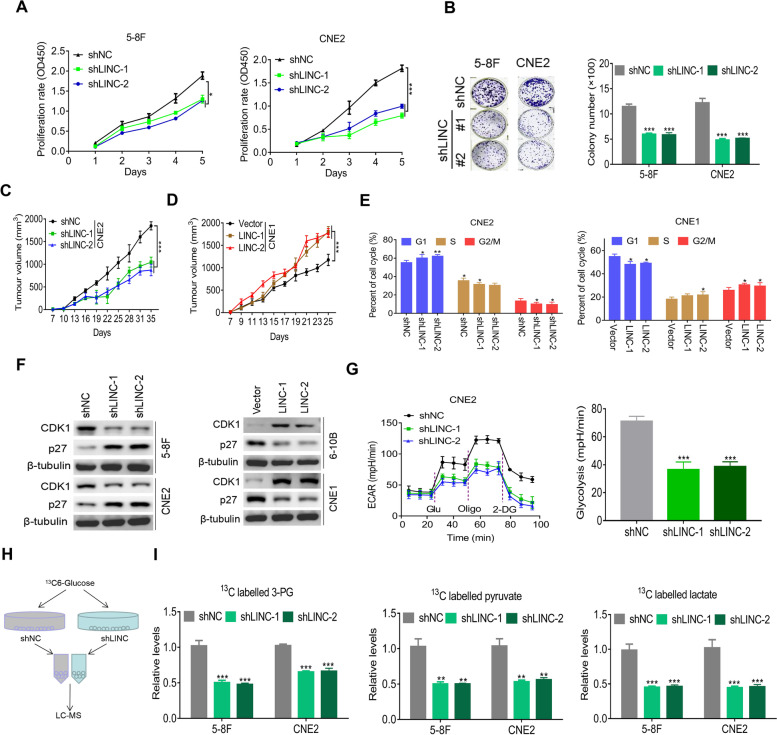
Fig. 2.
LINC00930 promotes cell proliferation and glycolysis. a and b Cell viability and colony formation in 5-8F and CNE2 cells stably knockdown LINC00930. c and d Subcutaneous tumor formation in nude mice. CNE2 cells with LINC00930 knockdown and CNE1 with LINC00930 overexpression were injected into one flank of the mouse. Tumor volume was measured and calculated at the indicated time (n = 8). e CNE2 cell with LINC00930 knockdown or CNE1 cell with LINC00930 overexpression were collected 48 h after releasing from synchronization with serum starvation. The cell cycle distributions were examined by flow cytometry analysis. DNA content was quantified using Modfit 3.2 software. Quantification of the cell population in each phase is presented. f CDK1 and p27 expression levels were detected by western blotting in 5-8F and CNE2 cells with LINC00930 knockdown (left) and in 6-10B and CNE1 cells with LINC00930 overexpression (right). g Left: The ECAR was measured in CNE2 cells with LINC00930 knockdown using an XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer. Right: Statistical analysis of the effects of LINC00930 knockdown on glycolytic activity. h Flowchart of the experiments for identifying the role of LINC00930 in glucose metabolism. i 13C-Labeled metabolic intermediates of glycolysis were decreased after LINC00930 knockdown. The p-value in a, c & d was determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, no adjustments were made for multiple comparisons. The p-value in b, e, g & i was determined by a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001