Fig. 1.
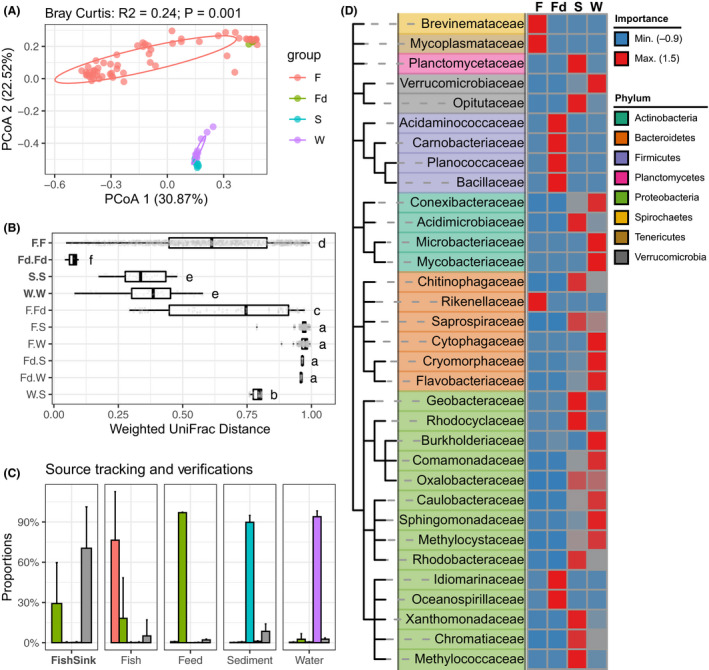
Comparisons of different bacterial communities within the fugu rearing ecosystems.
A. Two‐dimensional scatter plot of all bacterial communities based on principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. Percentage of explained variance and statistical significance were reported by PERMANOVA. A normal data ellipse for each group was drawn at confidence level of 0.68. Sample groups: ‘F’: Fugu gut; ‘Fd’: feed; ‘S’: sediment; ‘W’: water.
B. Boxplot shows the intra‐/inter‐groups pairwise comparisons of weighted UniFrac distances across all sample groups. For each box, the vertical bold bar denotes medians; the width of box denotes the interquartile range (25th percentile–75th percentile); the whiskers mark the values range within 1.5 times interquartile. Lower‐cased letters denote statistical significance reported by Mann–Whitney U‐test at confidence level of 0.95.
C. Source tracking of gut microbiota from rearing environments. The far left facet shows the SourceTracker‐estimated proportions of gut microbiota from its surrounding environment; the righter four facets, respectively, show the verifications using one each of the four sample groups as ‘source’. Bars denote average proportions of each source for a indicated community as sink (X‐axis) using trained source samples (F = 61, Fd = 3, S = 9, W = 9) rarefied by 1000 ESVs. Error bars represent standard deviations. Bars were coloured according to the indicated sources, of which ‘Unknown’ represent source unidentified from trained source data. Colour code is consistent with (A) excepting the ‘unknown’ source was showed in grey.
D. Random‐Forest identified bacterial families that accurately discriminated bacterial community groups. Featured taxa were hierarchically clustered according to NCBI taxonomy and were colour‐coded by phylum ranks. Heatmap showed the centred classic importance of each indicated taxa (row) in discriminating a given bacterial community (column) from others.
