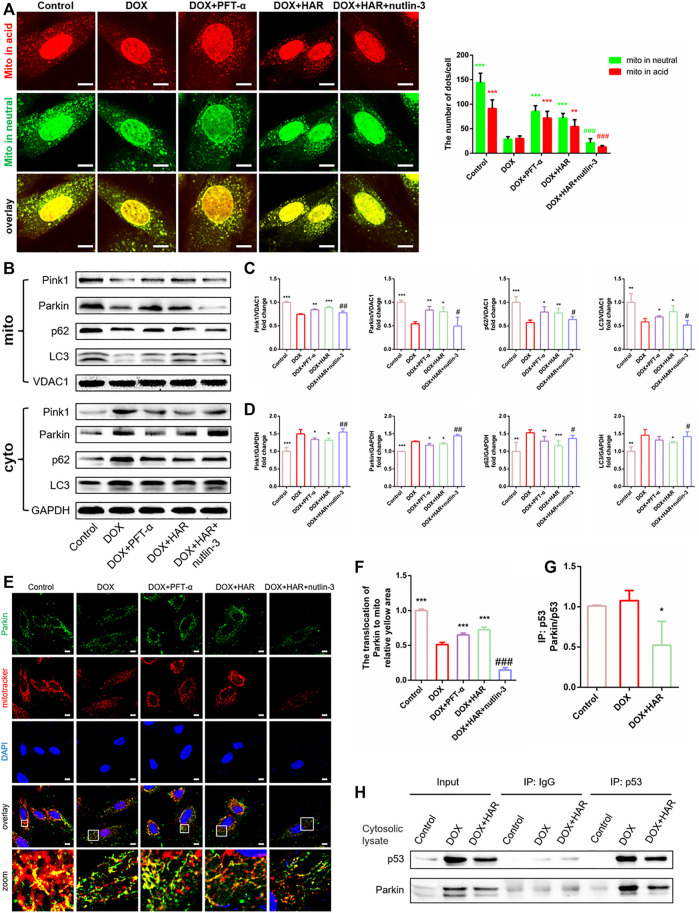
FIGURE 7.
HAR promoted Parkin-mediated mitophagy by inhibiting the binding of cytosolic p53 to Parkin in vitro. (A) Representative confocal images and quantitative analysis of mt-Keima puncta expressed in H9C2 cells treated with HAR, PFT-α or nutlin-3 (n = 6). (B–D) p53-dependent mitophagy-related proteins located in the cytosol and mitochondria were determined by immunoblotting, and their relative protein expression levels are shown after normalization to GAPDH or VDAC1 (n = 3–6). (E,F) Quantitative analysis of Parkin recruited to the mitochondria by costaining for Parkin and MitoTracker (n = 6). Scale bar: 10 μm. (G,H) Representative immunoblots and quantitative analysis of the binding of p53 and Parkin in the cytosolic lysates of H9C2 cells. Cytosolic lysates of H9C2 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-p53 and control IgG antibodies and immunoblotted with anti-Parkin and anti-p53 antibodies. The quantity of Parkin binding with p53 are normalizing to immunoprecipitated p53 (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. DOX group. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs. (DOX + HAR) group. The data are shown as the mean ± s.d.