Table 2.
Changes in the binding affinity (ΔGBIND) between the MAO isoforms and their physiological substrates following a complex formation with the WT and SA SARS-CoV-2 variants (in kcal mol−1).a, b
| Substrate | MAO A | MAO A⋅⋅⋅WT | MAO A⋅⋅⋅SA | MAO B | MAO B⋅⋅⋅WT | MAO B⋅⋅⋅SA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
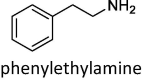 |
–16.8 ± 2.0 (KM = 140 μM) | –17.0 ± 1.7 | –15.8 ± 2.0 | –12.0 ± 1.2 (KM = 4 μM) | –9.4 ± 2.0 [–10.8 ± 2.1] | –14.8 ± 2.2 [–11.8 ± 1.5] |
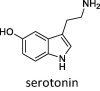 |
–20.1 ± 1.8 (KM = 137 μM) | –15.5 ± 2.1 | –23.0 ± 1.6 | – | – | – |
 |
– | – | – | –20.7 ± 2.2 (KM = 229 μM) | –15.4 ± 1.8 [–19.7 ± 1.2] | –23.0 ± 1.1 [–15.6 ± 1.0] |
Experimental KM values are taken from ref. [60] and are given in round brackets.
Results for the MAO B⋅⋅⋅WT/SA complexes pertain to the MAO B subunit directly interacting with the matching spike protein, while those for the other subunit are given in square brackets.
