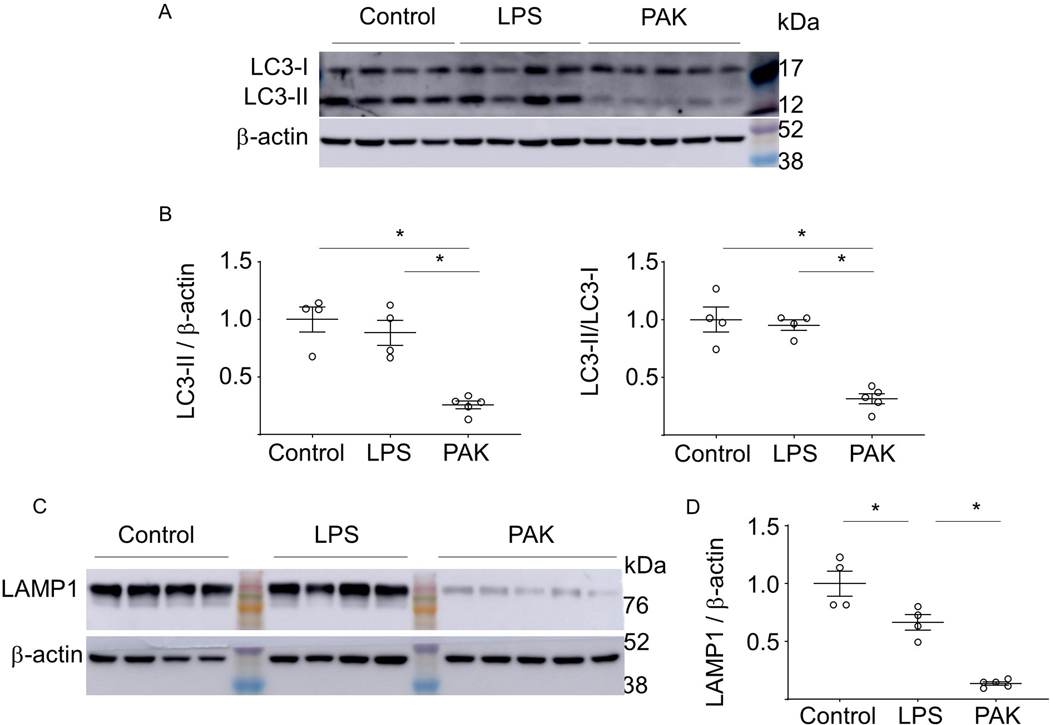
Figure 1.
The effects of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury and P. aeruginosa-mediated pneumonia on autophagy, phagolysosomal and lysosomal regulatory components in mouse lung. (A) Representative Western blots show LC3-I, LC3-II and β-actin levels in lung homogenates from control and mice subjected to intratracheal (i.t.) instillation of LPS for 24 hours, or after exposure to P. aeruginosa strain K (PAK) for 4 hours. The molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated. (B) Quantitative analysis of LC3-II/β-actin and LC3-II/LC3-I ratios. Data = mean ± sem, n = 4–5, *p < 0.05 (ANOVA). (C) Western blots and (D) quantitative analysis of LAMP1 in lung homogenates obtained from indicated groups of mice. Data = mean ± sem, n = 4–5, *p < 0.05 (ANOVA).