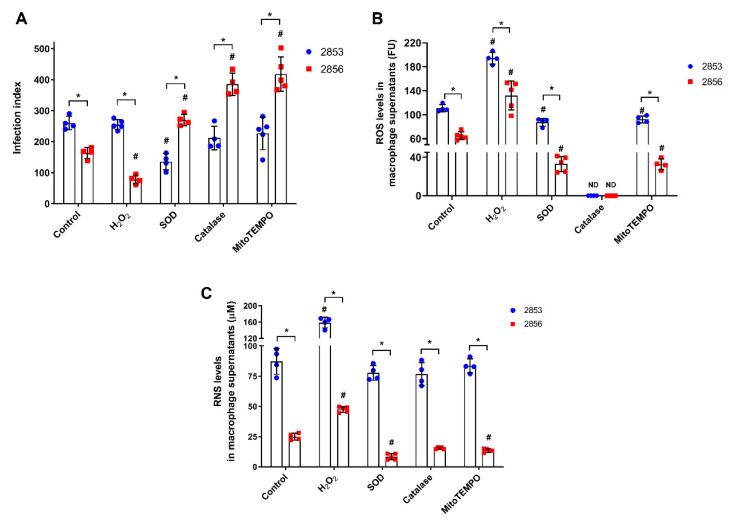
Figure 2.
Effect of ROS and RNS levels in peritoneal macrophages infected in vitro with L. braziliensis strains resistant and susceptible to NO. Peritoneal macrophages obtained from BALB/c mice were infected with promastigotes for 24 h. After that, cells were treated with 150 µM H2O2, 30 U/mL SOD, 40 U/mL catalase, or 1 µM mitoTEMPO for 48 h, completing 72 h of infection. Controls correspond to untreated cells infected for 72 h. (A) Infection index, which corresponds to percentage of infected host cells × number of parasites per 100 cells. (B) Host cells were incubated with 100 µM Amplex Red and 50 U/mL HRP for 30 min in respiration buffer and analyzed for detection of ROS levels. (C) Macrophage supernatants were collected, and the production of RNS was analyzed by Griess Reagent, according to manufacturer’s instructions. Graphs represent mean ± SD of at least four independent experiments. Significance of differences between strains were determined by t test using the Holm-Sidak method for multiple comparisons (* p ≤ 0.01). Significance of differences between treatments in comparison to control was determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (# p ≤ 0.05); ND = no detected.