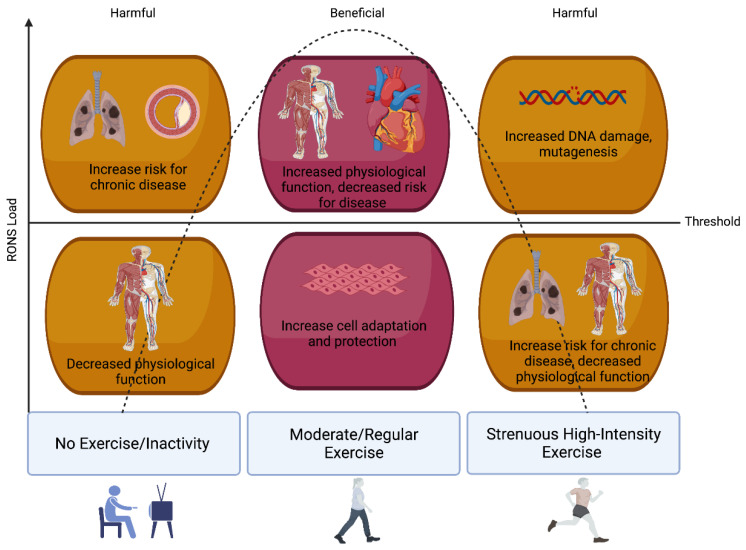
Figure 2.
Exercise-induced RONS, Oxidative Stress, and Hormesis. The fundamental basis of the hormesis theory can be applied to exercise-induced RONS formation: low or transient increases in RONS, from moderate-intensity and regular exercise, activate signalling pathways that induce adaptive and protective responses. Whereas inactivity and/or sporadic strenuous/high-intensity exercise can lead to a RONS load that overwhelms antioxidant defences leading to oxidative stress, impaired physiological function, and an increased risk for chronic disease.