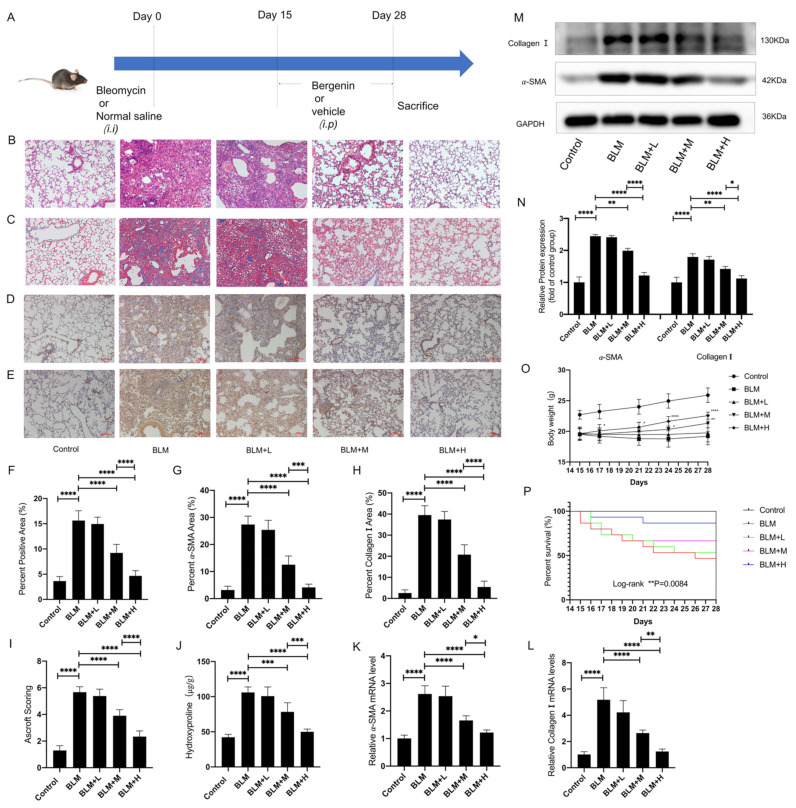
Figure 1.
Bergenin inhibits pulmonary fibrosis in mice. On days 15 to 28, after intratracheal injection of bleomycin, intraperitoneal injec-tions of bergenin were administered at high (25 mg/kg), moderate (5 mg/kg), and low (1 mg/kg) doses to evaluate its therapeutic effects on pulmonary fibrosis (A). HE staining and Masson staining were used to evaluate the lung morphology and ECM deposition (B,C,F). The fibrosis was scored using Ashcroft scoring (I), and immunohistochemistry was used to detect the positive expression of α-SMA and type I collagen in the lung tissue (D,E,G,H) (magnification ×100). The total hy-droxyproline content of the lung tissue was determined using biochemical methods (J). Western blotting and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Q-PCR) were used to detect the protein and mRNA expression levels of α-SMA and type I col-lagen (K–N). Changes in body weight and survival numbers of mice in each group were recorded daily (O,P). The following notations are used: Control for the control group; BLM for the bleomycin group; BLM + L for the bleomycin + 1 mg/kg bergenin group; BLM + M for the bleomycin + 5 mg/kg bergenin group; and BLM + H for the bleomycin + 25 mg/kg bergenin group. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 6–8, * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.