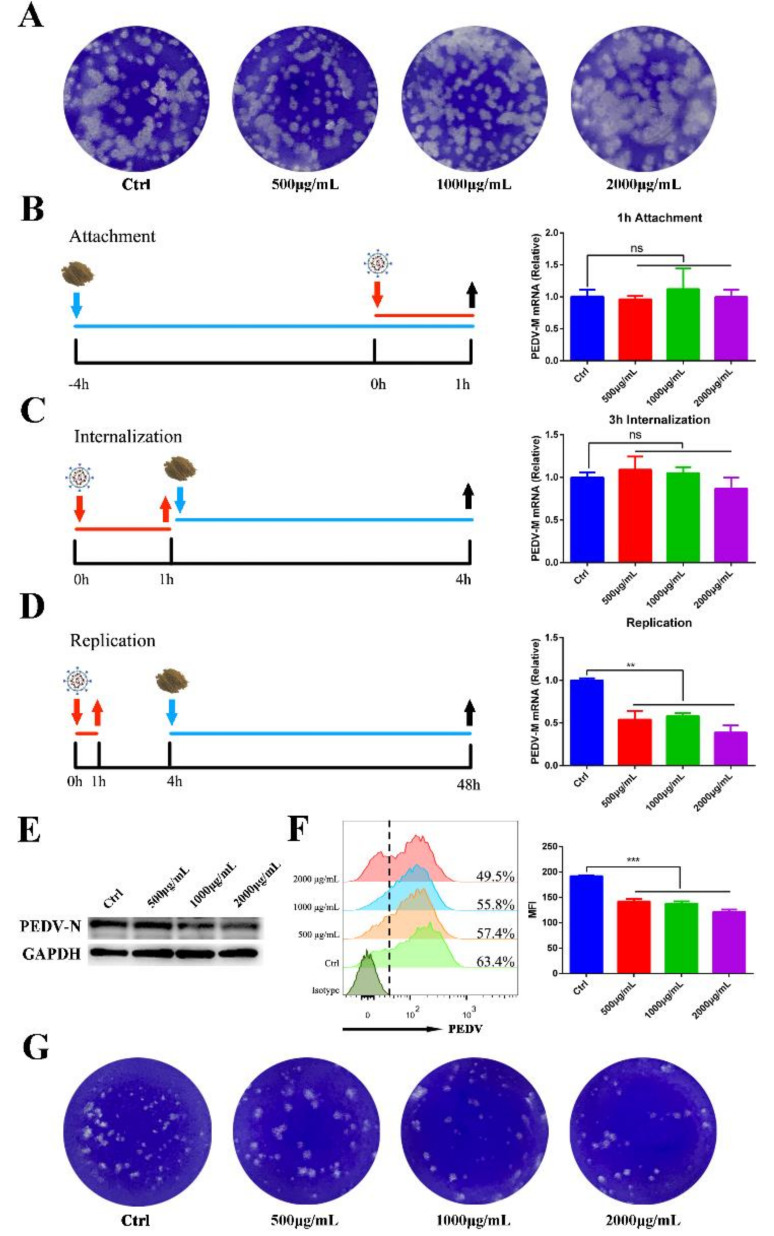
Figure 3.
Effect of MOE on the inactivation, attachment, entry, and replication of PEDV. (A) Inactivated assay. PEDV was incubated with indicated concentrations of MOE at 37 °C for 1 h; then, the mixture was added into confluent monolayers of Vero cells to detect the alive virions numbers by plaque assay. (B) Virus attachment assay. The supernatant was replaced with MOE during virus attachment stage. PEDV-M mRNA level was detected by qRT-PCR. (C) Virus internalization assay. The supernatant was replaced with MOE during virus internalization stage. (D) Virus replication assay. The supernatant was replaced with MOE during virus-replication stage. PEDV-M mRNA level was detected by qRT-PCR. (E) Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting assay. (F) Cells were subjected to flow cytometry. (G) Virus in the supernatant was detected by plaque assay. Data are expressed as three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; ns, no significance. MOE: the aqueous leaf extract of M. oleifera; PEDV: porcine epidemic diarrhea virus; MFI: mean fluorescence intensity.