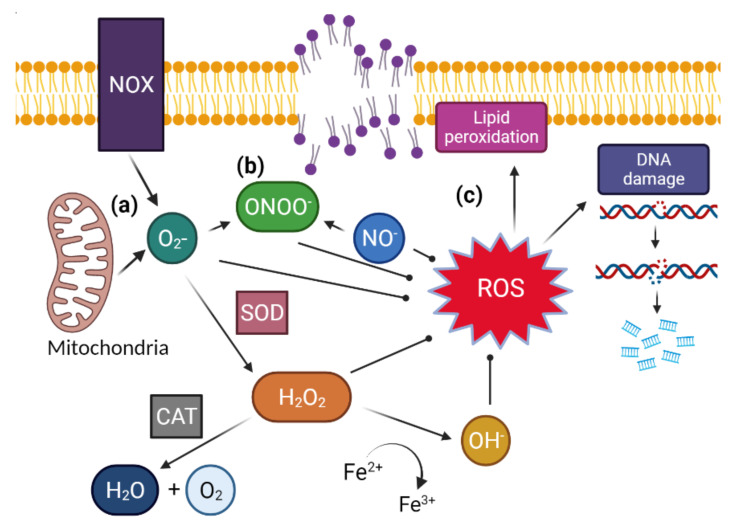
Figure 2.
(a) ROS formed within the cell starts as superoxide (O2−) created from ATP generation in mitochondria and from NADPH oxidase (NOX), and superoxide dismutates, facilitated by the protein superoxide dismutase (SOD) into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Hydrogen peroxide can then be neutralized by catalase (CAT) to create water (H2O) and singlet oxygen (O2). However, in the presence of ferrous iron it will react, creating hydroxyl radical (OH−). (b) If there is nitric oxide (NO−) present, then it will react to create peroxynitrite (ONOO−), a potent but unstable oxidant. (c) These ROS contribute to sperm damage through oxidation of the guanine base in DNA, creating single strand breaks, double strand breaks and DNA fragmentation, or through its oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids, creating lipid radicals that self-propagate, resulting lipid peroxidation.