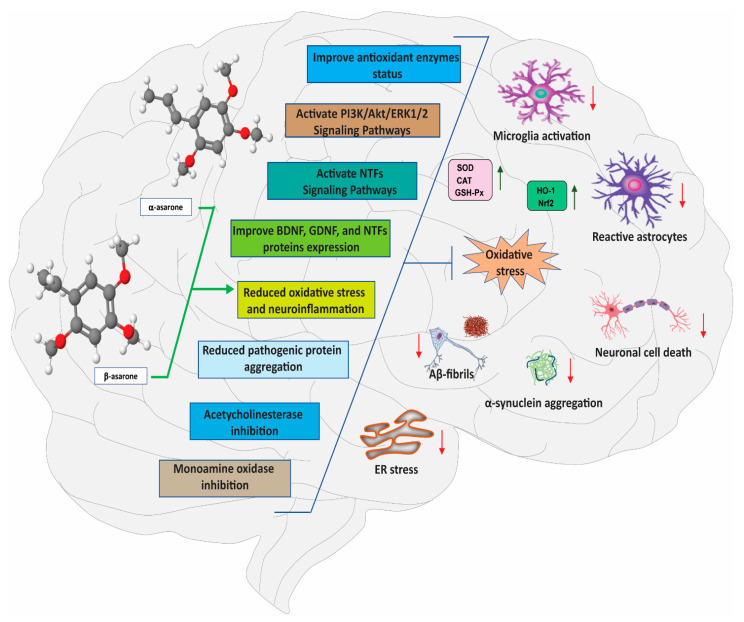
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanism of neuroprotection by α- and β-asarone. The multi-target effects of α- and β-asarone in the brain include anti-oxidant, mitochondrial protecting, anti-apoptotic, anti-aggregation, anti-inflammatory, and the regulation of various neuroprotective signalling pathways. Red down-arrow (↓) and green up-arrow (↑) signs indicate inhibition and activation by α- and β-asarone treatment, respectively. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GDNF, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; PI3K/Akt, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; NTFs, neurotrophic factors.