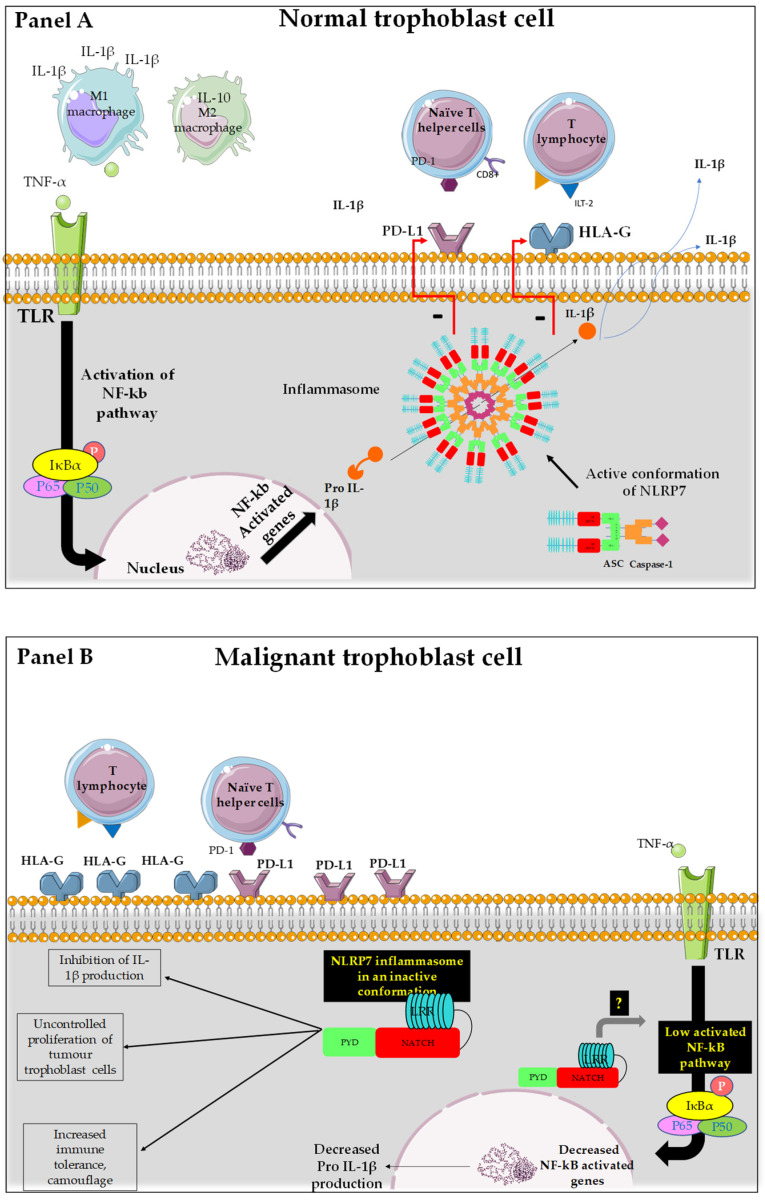
Figure 3.
Representation of the mode of function of NLRP7 in normal and tumor trophoblast cells. (A): NLRP7 is normally expressed in trophoblast cells and functions in an inflammasome-dependent manner to allow maturation of pro-IL-1β to IL1β. The transcription of pro-IL-1β depends on the activation of NF-κB that translocates into the nucleus and increases the transcription of pro-IL-1β. NLRP7 also regulates the expression of HLA-G and PD-L1 to allow normal tolerance of the trophoblast by the maternal immune system and favors the polarization of macrophages to M1 subtype. All these processes allow the protection of the fetus and ensure the progress of the pregnancy. (B): In malignant trophoblast cells, NLRP7 is overexpressed and functions in an inflammasome-independent manner. NLRP7 in turn mediates the increase in HLA-G and PD-L1 expression. This exacerbates maternal immune tolerance and camouflage of the tumor cells, creating a favorable, ant—inflammatory environment for tumor growth. NLRP7 overexpression mediates the excessive proliferation of trophoblast cells and suppresses their differentiation, allowing for further migration and invasion that ultimately leads to metastasis of distinct maternal organs.