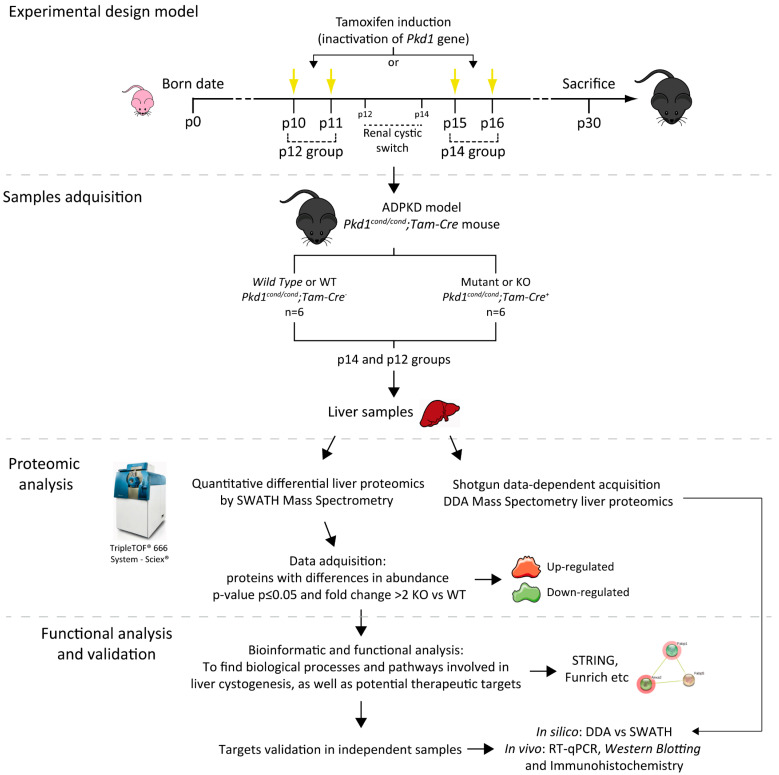
Figure 2.
Illustrated workflow scheme. We used an ADPKD murine model (Pkd1cond/cond;Tam-Cre mice) in which the genetic inactivation of Pkd1 was induced by tamoxifen administration at postnatal day 10 (p10) and p11 (rapid disease progression) or p15 and p16 (delayed disease progression) according to the developmental switch for renal cystogenesis, defining the two groups of the study named p12 and p14 respectively [19]. For both groups, we used an n equal or greater than six Wild Type (WT) and Mutant (KO) individuals in each condition, and all animals were sacrificed at p30. We studied the differential proteome of WT and KO livers in both severities of liver cystic disease (Figure 1), using both quantitative proteomic SWATH–MS and shotgun data-dependent acquisition DDA-MS analysis. Of the proteins with a significant change in abundance, we used bioinformatics tools to detect novel therapeutic targets and pathways involved in disease. Finally, we validated those targets using first in silico (DDA vs SWATH analysis) and finally in vivo strategies, as well as RT-qPCR, Western blotting and immunohistochemistry. p means postnatal day.