Figure 2.
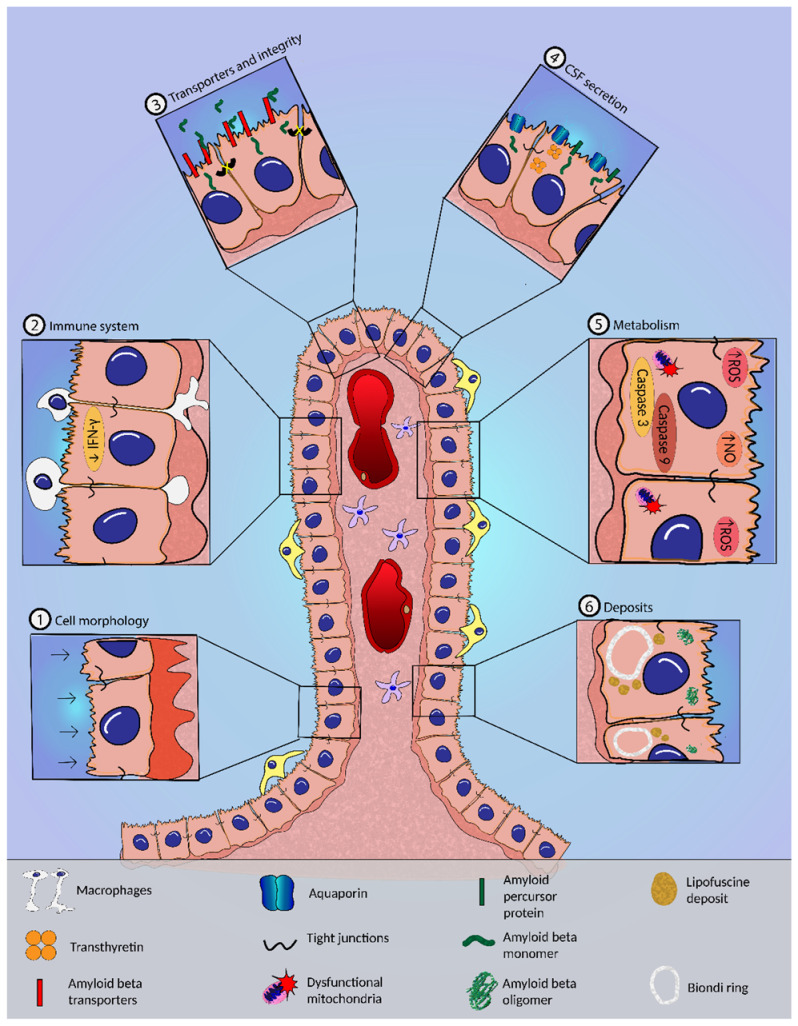
The choroid plexus (CP) and the blood–cerebrospinal barrier (BCSFB). The zoom highlights the alterations occurring in AD: (1) cell morphology—CP epithelial cell (CPEC) flattening and increased thickness and irregularity of the basement membrane; (2) immune system—impairment of leukocyte trafficking and decreased IFN-γ signaling; (3) transporters and integrity—tight junction disruption and deregulation of transporters of amyloid-β peptide (Aβ); (4) CSF secretion—diminished AQP1 expression, decreased secretion of CSF proteins, and increased production of Aβ in the CP; (5) metabolism—mitochondrial dysfunction and increased nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and caspase-3 and -9 expression; (6) deposits—deposits of Aβ, lipofuscin granules, and Biondi ring tangles accumulate in CPECs.
