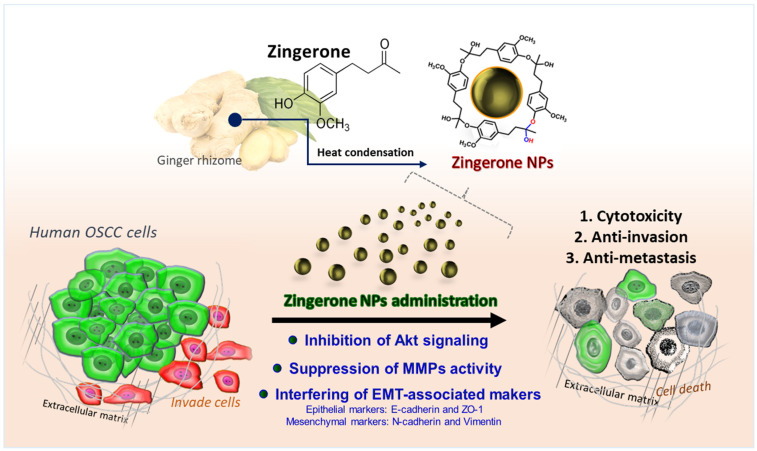
Figure 8.
The phytochemically derived zingerone NPs elicited superior efficacy to inhibit the cell invasion and metastasis of human oral squamous cell carcinoma. The as-fabricated zingerone NPs significantly suppressed Akt signaling-mediated cell survival and cell motility, which led to obvious cytotoxicity and anti-proliferation. Moreover, the zingerone NP-mediated downregulation of MMP activity was also reflected in the harsh cell motility. In addition, the zingerone NPs substantially disturbed the expression levels of EMT-associated markers, including the mesenchymal markers N-cadherin and vimentin, and the epithelial markers ZO-1 and E-cadherin. These results suggested that the zingerone NPs exerted superior suppression on cell proliferation, tumorigenicity, and cell motility, and thus achieved an inhibitory effect against the cell invasion and metastasis of human oral squamous cell carcinoma.